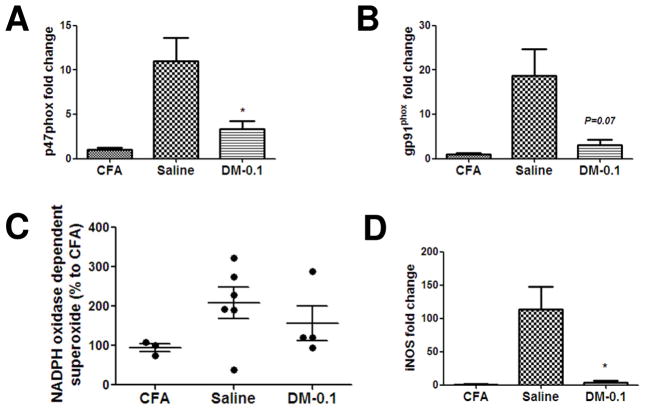
Figure 5. DM-0.1 inhibits the expression of NOX2 and oxidative stress response in the spinal cord tissue of EAE-II animals.
Mice were immunized with 50 μg MOG/0.5 mg/ml M.t. and treated with saline or DM-0.1 starting from day 7 until the peak of EAE (19–20 d.p.i.). Lumbar spinal cords were collected after perfusion with PBS and analyzed for the expression and activity of NOX2. DM-0.1 treatment (n = 4) could significantly reduce the mRNA level of p47phox in the spinal cord tissue when compared to saline (n = 6) (A). The transcription level of the enzymatic subunit gp91phox was also decreased in the spinal cord tissue after DM-0.1 treatment (B). A non-significant reduction in NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide production was found in the spinal cord homogenates of DM-0.1 treated animals (D). The transcription level of iNOS was dramatically decreased by DM-0.1 treatment (E). *, p < 0.05 versus the saline group.