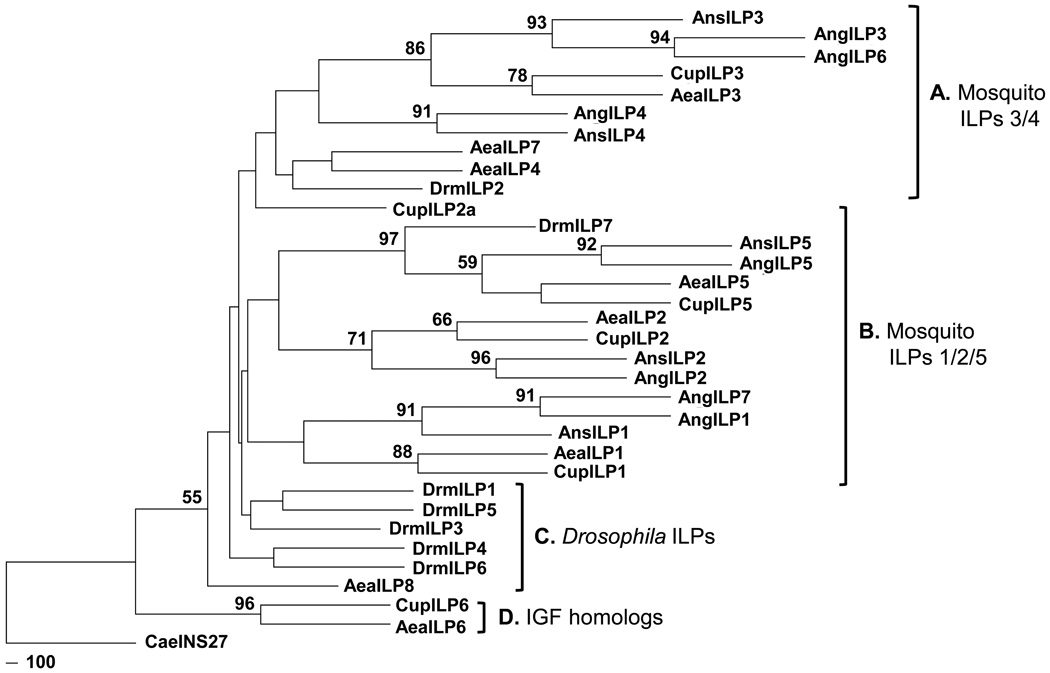
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of mosquito and D. melanogaster insulin-like peptides (ILPs) generated with the maximum likelihood method and bootstrap analysis.
Nodes with bootstrap support higher than 50% are shown at the base of the branches and represent the percentage of times that grouping was supported. A–D represents the clade classifications based on the groupings of different ILPs. Abbreviations and NCBI accession numbers of species indicated are as follows: Ae. aegypti (AeaILP1 DQ845750; AeaILP2 DQ845752; AeaILP3 DQ845751; AeaILP4 DQ845753; AeaILP5 DQ845758; AeaILP6 DQ845755; AeaILP7 DQ845757; AeaILP8 DQ845754), An. gambiae (AngILP1 AY324307; AngILP2 AY324308; AngILP3 AY324309; AngILP4 AY324310; AngILP5 AY324312; AngILP6 AY324313; AngILP7 AY324314), An. stephensi (AnsILP1 HM030813; AnsILP2 HM030814; AnsILP3 HM030815; AnsILP4 HM030816; AnsILP5 HM030817), Cu. pipiens (CupILP1 6051901; CupILP2 6051914; CupILP2a 6051902; CupILP3 6051906; CupILP5 6032673; CupILP6 6034782), and D. melanogaster (DrmILP1 NP_648359; DrmILP2 NP_524012; DrmILP3 NP_648360; DrmILP4 NP_648361; DrmILP5 NP_996037; DrmILP6 NP_570000; DrmILP7 NP_570070). INS27 from C. elegans (CaeINS27 Z82082) was used as an outgroup.