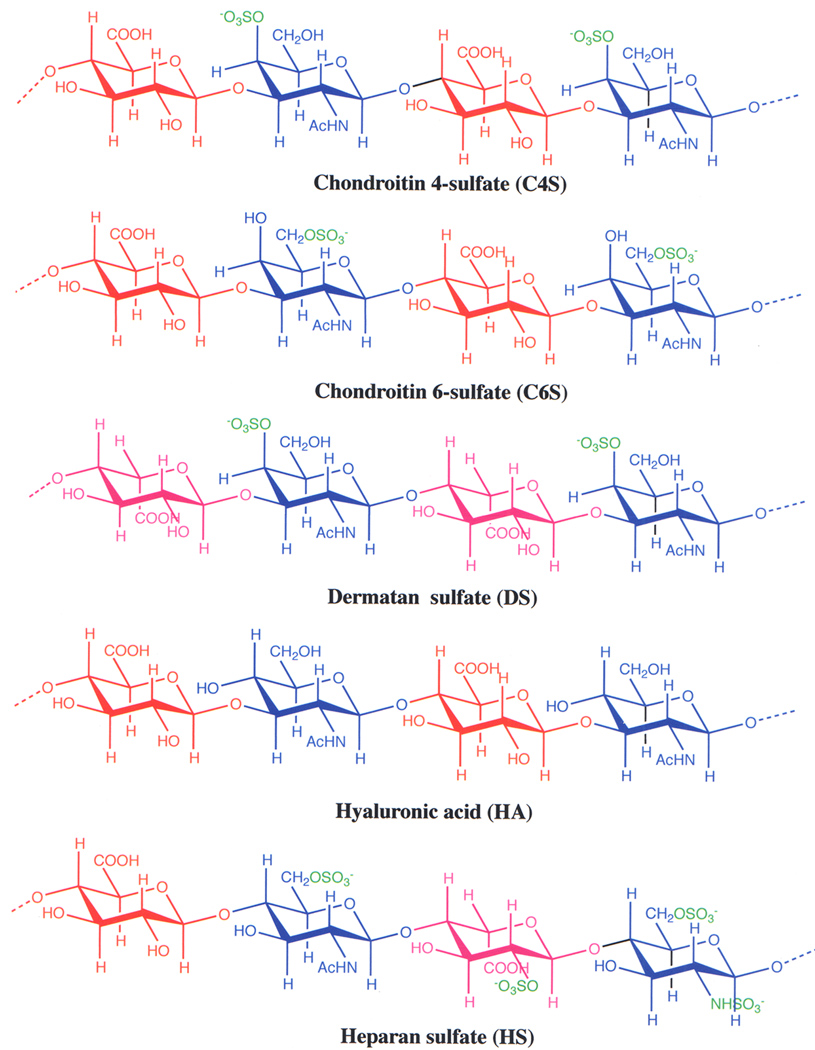
Figure 1.
The structures of tetrasaccharide segments, representing two repeating units, of various glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Red, D-glucuronic acid; Pink, L-iduronic acid; blue N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (in C4S, C6S, and DS), N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (in HA and HS) or N-sulfated D-glucosamine (in HS); green, sulfate group. In C4S and C6S, the glucuronic acid residues are linked to N-acetylgalactosamine residues by β(1–3) glycosidic bonds, whereas the N-acetylgalactosamine residues are linked glucuronic acid residues by β(1–4) glycosidic bonds. In DS, the iduronic acid residues are linked to N-acetylgalactosamine residues by α(1–3) glycosidic bonds, while N-acetylgalactosamine residues are linked to iduronic acid residues by β(1–4) glycosidic bonds. In HA, the glucuronic acid residues are linked to N-acetylglucosamine residues by β(1–3) glycosidic bonds, whereas N-acetylglucosamine residues are linked to glucuronic acid residues by β(1–4) glycosidic bonds. In HS, the glucuronic acid residues are linked to N-acetylglucosamine residues by β (1–4) glycosidic bonds, iduronic acid residues are linked to either N-acetylglucosamine or N-sulfated glucosamine residues by α(1–4) glycosidic bonds, and N-acetylglucosamine or N-sulfated glucosamine residues are linked to either glucuronic acid or iduronic acid residues by β(1–4) glycosidic bonds. Note that D-glucuronic acid and L-iduronic acid residues are differed by one another only in the configuration of the carboxyl group present at the C-5 position. In placental C4S chains, not all N-acetylgalactosamine residues are sulfated as shown above for a fully sulfated C4S, but only a few residues are sulfated exclusively at C-4, resulting in low sulfated C4S chains.