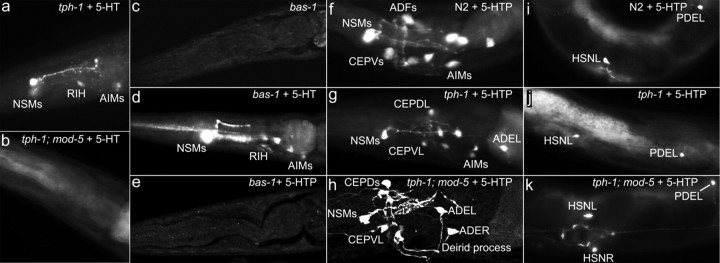
Figure 3.
Differential ability of 5-HT-producing neurons to take up 5-HT and 5-HTP. Representative photomicrographs of 5-HT immunostaining of WT and indicated mutants untreated and treated with 2 mg/ml 5-HT or 0.1 mg/ml 5-HTP for 5.5 h. All the animals shown have anterior to the left. a, b, tph-1 and tph-1;mod-5 mutants treated with exogenous 5-HT. Applying 5-HT restored 5-HT immunoreactivity in tph-1 mutants but not in tph-1;mod-5 double mutants. c–e, bas-1/decarboxylase mutants untreated and treated with 5-HT or 5-HTP. Untreated bas-1 mutants showed no discernable 5-HT immunoreactivity. bas-1 mutants treated with 5-HT restored 5-HT immunoreactivity. 5-HTP treatment did not improve 5-HT immunoreactivity in bas-1 mutants. f–k, 5-HTP treatment of WT, tph-1 mutants, and tph-1;mod-5 double mutants. The head region (f–h) and the middle-to-posterior portion of the body (i–k). 5-HT immunoreactivity was observed in all of the 5-HT-producing neurons in these genetic backgrounds. In addition, 5-HT immunoreactivity was detected in the dopaminergic neurons (CEP, ADE, and PDE), consistent with the expression pattern of bas-1/decarboxylase (Hare and Loer, 2004). Quantification of the percentage of each neuronal types stained in the strains is presented in Table 2.