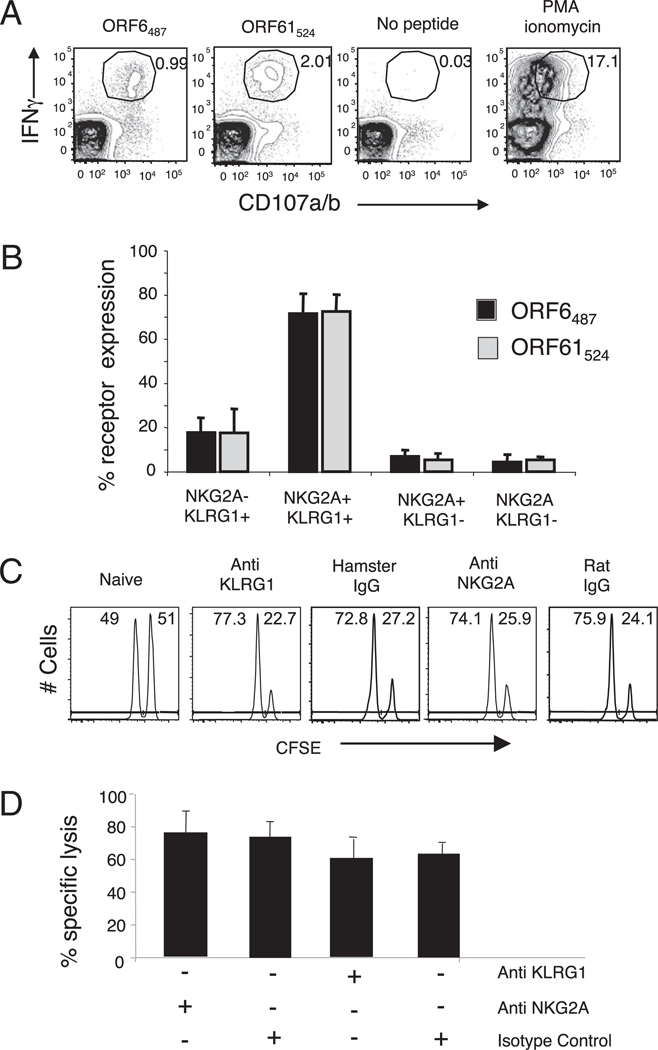
FIGURE 4.
KLRG1+NKG2A+ cells constitute the majority of the IFN-γ/CD107a/b polyfunctional CD8 T cells during γHV68 persistent infection. A, Representative plots show intracellular IFN-γ production and cell surface CD107a/b mobilization on previously gated CD8 T cells. Splenocytes isolated from mice infected with γHV68 3 mo earlier were stimulated with γHV68-specific ORF6487–495 and ORF61524–531 peptides. B, Bar diagram displays the frequency of KLRG1 and NKG2A receptor expression among IFN-γ/CD107a/b polyfunctional CD8 T cells. Bars represent the mean value of three experimental samples, and error bars indicate SD. C, Representative histograms of CFSE intensity of an in vivo CTL assay in the presence or absence of Abs against KLRG1 and NKG2A. D, Bar diagram shows the percentage specific lysis of ORF6487–495-loaded target cells injected into γHV68-infected mice at 3 mo p.i. that were previously treated or not treated with Abs against KLRG1 and NKG2A. Data are the mean of three individual mice per experiment, and error bars represent SD. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments.