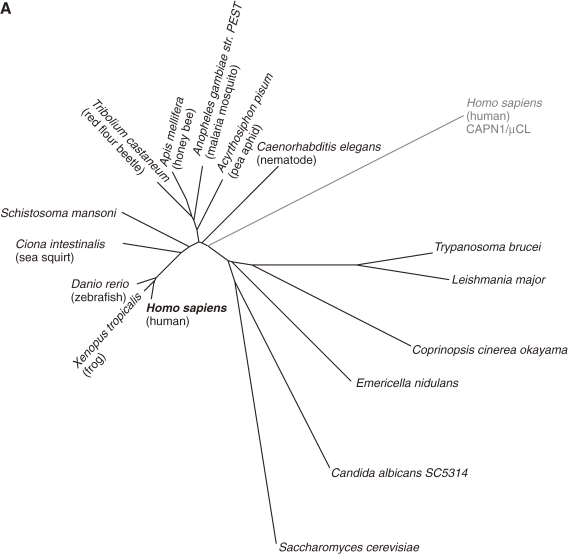
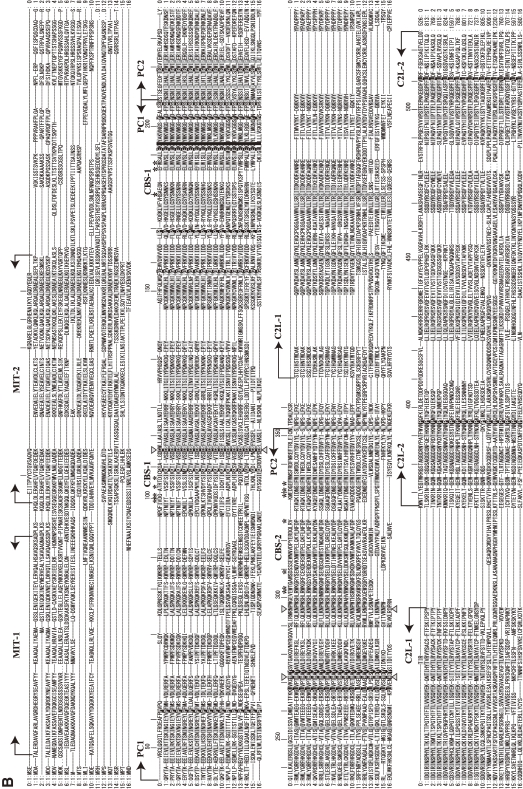
Figure 12.
Phylogenetic tree and sequence alignment of PalB calpains. A. Phylogenetic tree of strict PalB calpains and human CAPN1/μCL. See Fig. 3A for methods. B. Sequence alignment of PalBs and human CAPN1/μCL (the start and end aa residue numbers are indicated). Triangles: active site residues. Asterisks: residues involved in Ca2+-binding of the protease domain of CAPN1/μCL. Arrows: domain boundaries. Deletion (−) and multiple (+) residue positions are indicated. Residue numbers of human CAPN1/μCL are given above the sequences. Residues conserved in all the sequences, all except human CAPN1/μCL, and in more than half the sequences are indicated by black reversed fonts, gray reversed fonts, and gray shadow, respectively. Sequences: 0: H. sapiens (human) CAPN1/μCL (NP_005177); 1: H. sapiens CAPN7/PalBH (NP_055111); 2: X. tropicalis (frog) (NP_998853); 3: D. rerio (zebrafish) (NP_001128580); 4: Ciona intestinalis (sea squirt) (XP_002121253); 5: Tribolium castaneum (red flour beetle) (XP_967682); 6: Apis mellifera (honey bee) (XP_001121978); 7: Acyrthosiphon pisum (pea aphid) (XP_001945029); 8: A. gambiae str. PEST (malaria mosquito) (XP_309874); 9: S. mansoni (XP_002579452); 10: C. elegans (NP_497964); 11: T. brucei TREU927 (XP_828540); 12: L. major (CAJ06528); 13: Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130 (common ink cap) (EAU91907); 14: E. nidulans FGSC-A4 (XP_657860); 15: C. albicans SC5314 (EAL03290); 16: S. cerevisiae (Q03792).