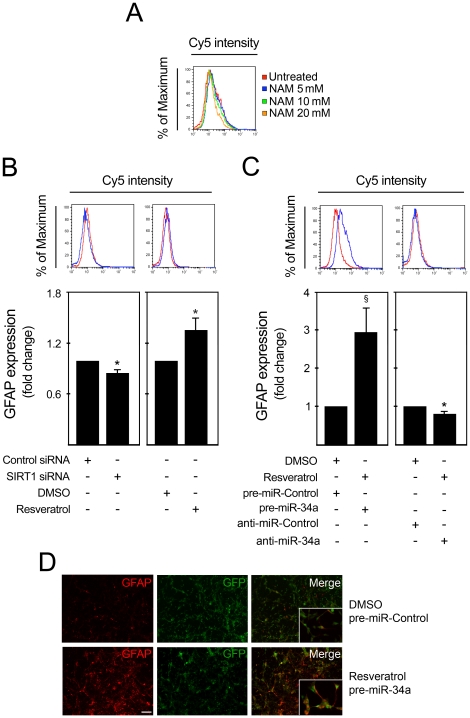
Figure 5. miR-34a promotes astrocytic differentiation under resveratrol treatment.
SIRT1 expression was modulated in mouse NS cells after 12 h of induction of differentiation. Inhibition of SIRT1 was achieved by incubation with nicotinamide or by transfecting cells with either scrambled control or 100 nM of SIRT1 siRNA. SIRT1 was activated by treating cells with either DMSO (control) or 5 µM of resveratrol. Cells were collected at 3 days, fixed and processed for GFAP labeling and detection by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. The blue line corresponds to SIRT1 modulation, while the red line represents the respective control. A. Incubation with nicotinamide, decreased the percentage of GFAP+ cells in a dose-dependent manner. B. Decreased percentage of GFAP+ cells after silencing of SIRT1 (left), and increased percentage of GFAP+ after SIRT1 activation (right). C. Under resveratrol treatment, overexpression of miR-34a resulted in increased proportion of GFAP+ cells (right), while miR-34a downregulation had the opposite effect (left). D. Immunofluorescence showing increased number of GFAP+ cells under resveratrol treatment and miR-34a overexpression (bottom) when compared with controls (top). Scale bar, 80 µm. Images taken with a magnification of 400× are shown in detail. *p<0.05 and § p<0.001 from cells transfected with respective control. NAM, nicotinamide.