Fig 3.
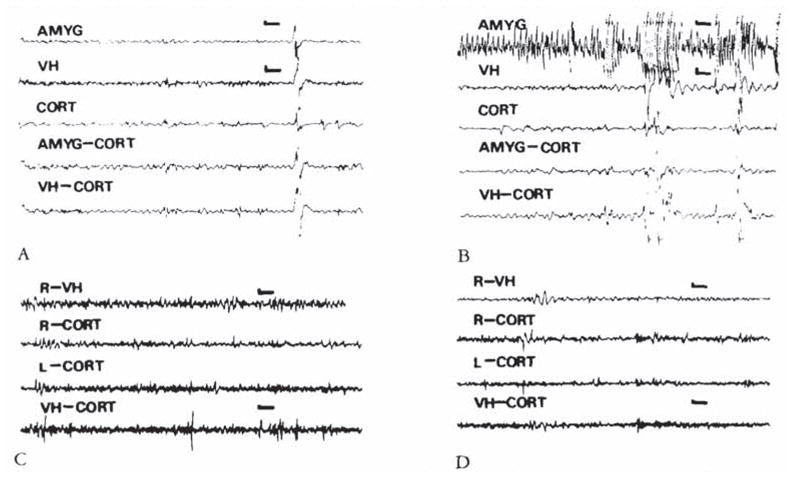
(A, B) Electroencephalograms (EEGs) of an 8-day-old infant rat. carrying both bipolar amygdala (AMYG) and ventral hippocampus (VH) electrodes, before administration of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (A) and 8 minutes after administration of 0.15 nm of the peptide (B). Paroxysmal discharges originate in the amygdala leads. Movement artifacts are later seen in all leads. (C, D) EEGs of an 11-day-old rat before (C). and 26 minutes subsequent to the administration of 0.15 nm of CRH. Though the pup displayed jaw myoclonus, only attenuation of the theta rhythm is seen in the ventral hippocampus (VH). CORT = cortex; AMYG-CORT/VH-CORT = a lead combining one of the subcortical electrodes to the cortical one. Vertical bar = 50 μV; horizontal bar = 1 second.
