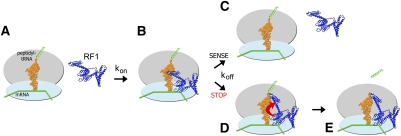
FIGURE 7.
Proposed mechanism for coordination of peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis with stop-codon recognition via a conformational switch in class I release factors. (A,B) Initially, the release factor binds to the ribosome in a catalytically inactive conformation. (C) If a sense codon is located in the A site, the release factor quickly dissociates (Hetrick et al. 2009). (D) If the release factor recognizes a stop codon in the A site, its switch loop along with domain 3 and the decoding center rearrange. Interaction between the switch loop and the switch-loop binding pocket in the decoding center results in tight binding of the release factor to the ribosome. (E) In this catalytically competent conformation, the GGQ motif is inserted in the peptidyl-transferase center and is capable of contributing to catalysis of peptidyl-tRNA ester bond hydrolysis.