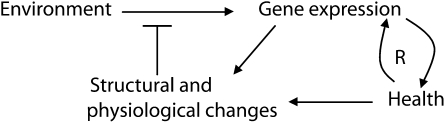
FIGURE 1.
The interplay of genes and environments: recursive developmental remodeling.
Note. A single-headed arrow from X to Y indicates that X is a cause of Y or that X causes increased exposure to Y. A line intersecting a 1-headed arrow (in the form of a T) indicates that the factor modifies or modulates the relation between X and Y (effect modification in epidemiologic terms). The T-shaped line from structural/physiological changes that intersects the arrow from environment to gene expression indicates that the structural and physiological changes modify or modulate the effect of environments on gene expression. Positive or negative feedback loops are indicated with an R (reinforcing) or a B (balancing). Reinforcing loops promote or reinforce change in one direction. Balancing loops tend to close the gap between the current state and the desired state. Directionality (plus or minus signs associated with the arrows) is not indicated in the figures but the types of relations can be inferred from the description in the text.
Source. Adapted from Cole.43