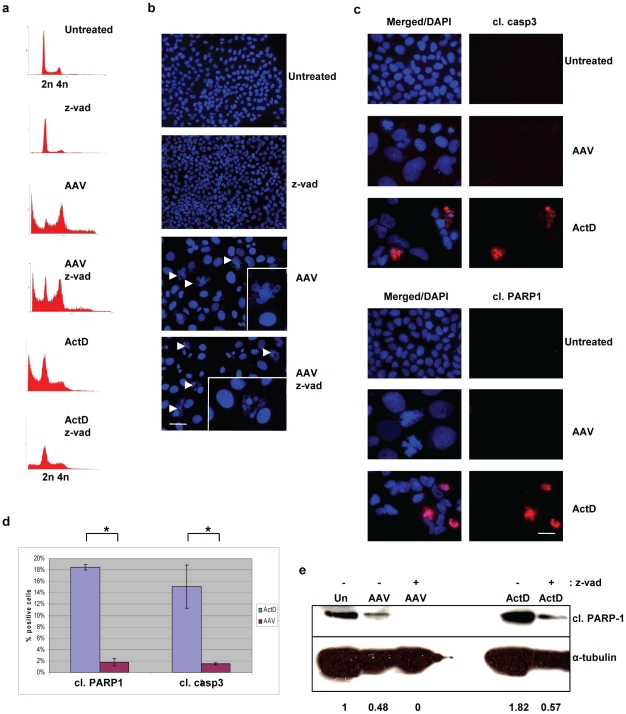
Figure 2. Mitotic cell death induced by AAV is caspase-independent.
(a) FACS analysis showing that inhibition of caspases does not prevent cell death. U2OSp53DD cells were infected with AAV and then treated with zVAD-fmk 2 days post-infection. The cells were analyzed by PI staining and FACS, 4 days post-infection (x-axis: DNA content; y-axis: cell count). Treatment with zVAD-fmk prevented the ActD-induced cell death that was used as a control. Treatment with zVAD-fmk alone did not have an effect on the cell cycle. (b) Caspase inhibition does not prevent micronucleation. AAV-infected U2OSp53DD cells were treated with zVAD-fmk 2 days post-infection and analyzed by DAPI staining and IF 4 days after infection. Arrows indicate micronucleated cells. Images were acquired using a 10× objective. Bar: 215 µm. The inserts show cells at higher magnification. (c) AAV-infected U2OSp53DD cells are negative for cleaved caspase-3 (casp3) and cleaved PARP-1. Cells were infected and stained for the two markers of caspase-dependent apoptosis and DAPI, 4 days after infection. Bar: 25 µm. (d) The percentage of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP-1 –positive cells from the experiment described in (c). Error bars represent standard deviations from two independent experiments. The asterisk denotes statistically significant difference (2-tailed t-test) (e) Western blotting showing low levels of cleaved PARP-1 in AAV-infected U2OSp53DD cells. Treatment with zVAD-fmk decreased the levels of cleaved PARP-1. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. The relative levels of cleaved PARP-1 normalized using the loading controls are shown below. Un: untreated.