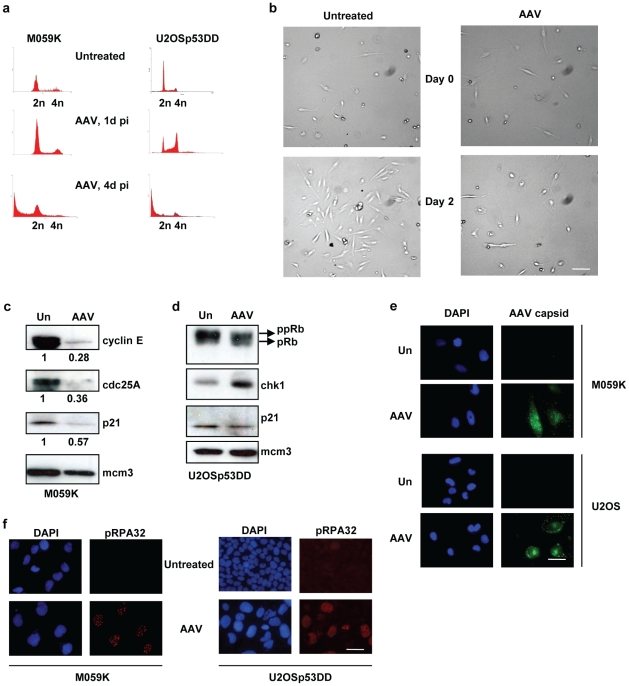
Figure 7. M059K cells have, unlike U2OSp53DD cells, a functional G1 checkpoint.
(a) PI staining and FACS analysis of AAV-infected M059K and U2OSp53DD cells (x-axis: DNA content; y-axis: cell count). U2OSp53DD cells arrest at G2 1 day post-infection, whereas M059K cells do not. Both cell types proceed to death 4 days after infection. (b) Brightfield-microscopy images of untreated and AAV-infected M059K cells showing that infected cells arrest up to 2 days after infection. Images were acquired using the 10× objective. Bar: 230 µm. (c) M059K cells arrest in G1 after AAV-infection. Cells were infected and total protein was extracted 1 day post-infection. Western blotting showed low levels of cyclin E and cdc25A in infected cells, which is indicative of a functional G1 checkpoint. Mcm3 was used as a loading control. The numerical values below the bands are the relative protein amounts normalized to the loading control. Un: untreated. (d) The same experiment was performed in U2OSp53DD cells. High levels of phosphorylated pRb (ppRb) and of chk1 1 day post-infection indicate that these cells have a weak G1 checkpoint and arrest in G2. (e) Control experiment showing that M059K cells are efficiently infected with AAV. Cells were infected with untreated-AAV and stained using an AAV-capsid antibody, 1 day after infection. U2OSp53DD cells were used as a control. DAPI was used to stain nuclei. Bar: 35 µm. (f) Control IF experiment showing that AAV induces a similar DNA damage response in M059K cells to that induced in U2OSp53DD cells. Induction of phospo-RPA32 (pRPA32) foci was used as a marker for DNA damage response. DNA was stained using DAPI. The experiment was performed 1 day post-infection. Bar: 35 µm.