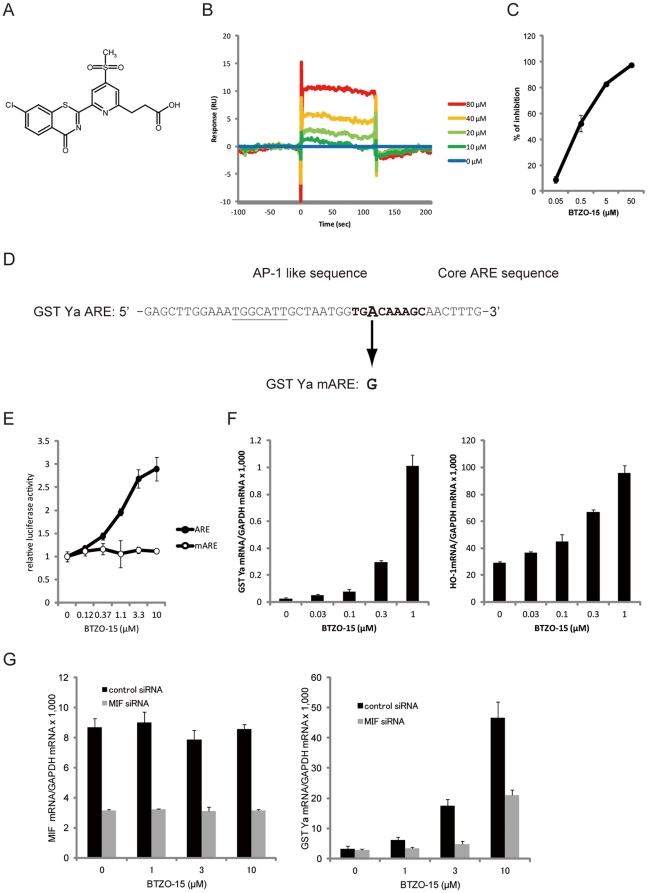
Figure 1. BTZO-15 activates the GST Ya ARE by interacting with MIF.
(A) Chemical structures of BTZO-15. (B) Sensorgram showing binding of BTZO-15 to immobilized hMIF on a CM5 sensor chip using an SPR biosensor. (C) Displacement studies with BTZO-15 by the SPA showing inhibition of BTZO-1 binding to captured rMIF on SPA beads. Results shown are the mean ± SD, n = 3. (D) Nucleotide sequence of the rat GST Ya ARE. The core ARE sequence is indicated by the nucleotides in boldface type. (E) Reporter gene assays showing the effect of BTZO-15 on ARE activity. H9c2 cells transiently transfected with either pGL3-ARE-Luc or pGL3-mARE-Luc reporter plasmids were treated with the indicated concentrations of BTZO-15 for 24 h and luciferase activities were measured. Results shown are the mean ± SD, n = 3. (F) BTZO-15 induced ARE-regulated cytoprotective proteins in H9c2 cells. The cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of BTZO-15 for 6 h (HO-1) or 21 h (GST Ya). HO-1 mRNA levels were measured by real-time PCR and normalized by GAPDH mRNA. Results shown are the mean ± SD, n = 3. (G) Effects of reducing the cellular MIF protein level on BTZO-15-induced GST Ya and HO-1 gene expression in H9c2 cells. H9c2 cells transfected with control siRNA (control siRNA) or siRNAs directed against rMIF (MIF siRNA) were treated with 3 µM BTZO-15 with or without 0.8 µM rMIF for 24 h. Messenger RNA levels of MIF, GST Ya, and HO-1 were measured by real-time PCR. MIF protein level in cell lysates was measured by ELISA.