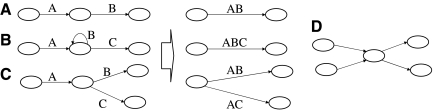
FIG. 4.
(A–C) These demonstrate the three cases of graph simplification described in Section 7. Case A is a chain, case B a loop attached to a chain, and case C is a split vertex. A join vertex case is symmetrical and is not shown. The three simplifications are shown to the right. In all cases, the new graph can “spell” the exact same strings as the initial graph. (D) This is a conflict node. By iterative application of cases A, B, and C, we generate a graph where all remaining vertices are of type D.