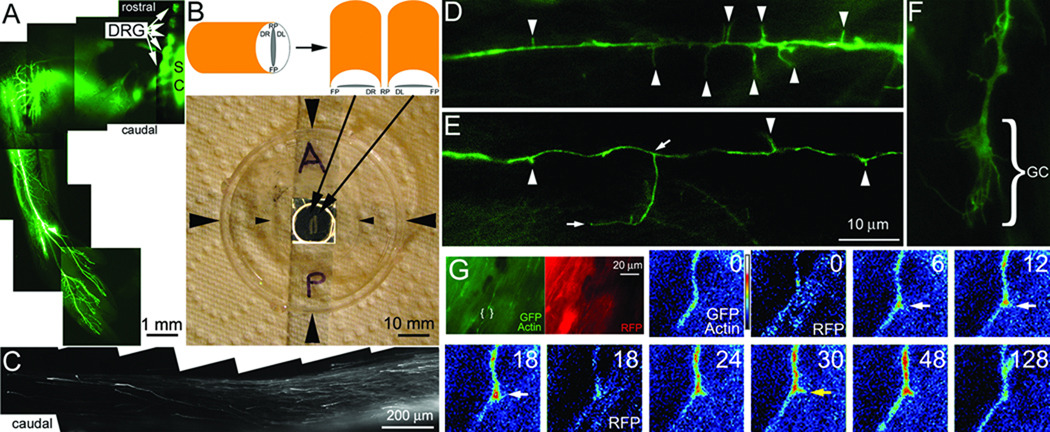
FIGURE 1. Acute ex vivo spinal cord model.
(A) Example of the ventral portion of the hind limb of an ED 9 embryo whole mount transfected with GFP at day 3. The image is a montage of 4× images. Transfected DRGs are readily detected (arrows) as are transfected cells in a few segments of the spinal cord (SC). GFP labeled nerves are detectable throughout the limb. (B) The schematic shows the orientation of the bisected cord when placed on the glass coverslip of the chamber system. The photograph shows the assembled chamber system. Large arrowheads denote the sides of the chamber. The small arrowheads denote the sides of the coverslip laid on top of the well in the chamber forming a sealed environment. The well in the center of the dish is contrast enhanced. Resting within the well is a bisected spinal cord as shown in the schematic. A=anterior/rostral, P=posterior/caudal. (C) Example of GFP-labeled DRG axons extending in the caudal dorsal funniculi of an explanted spinal cord. The image is a montage of 20× images. Note the absence of other GFP-transfected cells. (D) Example of axonal filopodia (arrowheads) extending from a GFP-transfected axon (100×). (E) Example of axonal filopodia and a branch approximately 18 µm in length (100×). The base and tip of the branch are denoted by arrows. (F) Example of a growth cone (GC; 100×; also see Figure 4E). (G) The green and red panels show the 100× imaging field for the GFP-actin and RFP channels respectively. The area of interest shown in the false colored panels is denoted by brackets. The timelapse sequence shows the GFP-actin and RFP channels representing a co-transfected axon. Time is in seconds. An actin patch forms at 6 sec, gives rise to a filopodium at 30 sec (yellow arrow) and dissipates by 128 sec. The RFP channel (0 and 18 sec) does not reveal a similar localized increase in fluorescence.