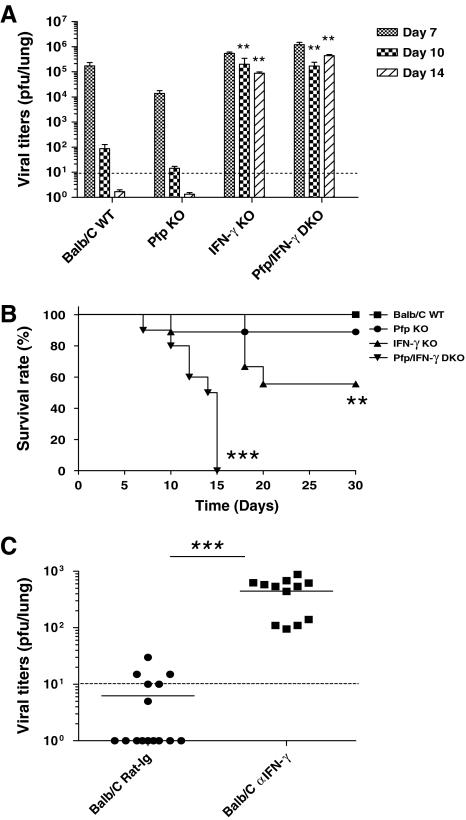
FIG. 1.
Control of respiratory MHV-68 infection depends upon IFN-γ in BALB/c mice. (A) Mice were infected with 400 PFU of MHV-68 intranasally. Lungs were harvested at days 7, 10, and 14 after infection, homogenized, and assayed for virus titer. The limit of detection was 10 PFU per lung (dashed line). (B) Survival of infected mice was observed over a period of 30 d. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve is shown for groups of 10 to 15 mice. (C) BALB/C mice were given IFN-γ-blocking antibody at days −1, 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 relative to infection, and infected with 400 PFU MHV-68 intranasally at day 0. Lungs were removed at day 10 and plaque assays performed. Each dot represents data from an individual animal and horizontal bars indicate the mean. Data are representative of 3–4 experiments (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).