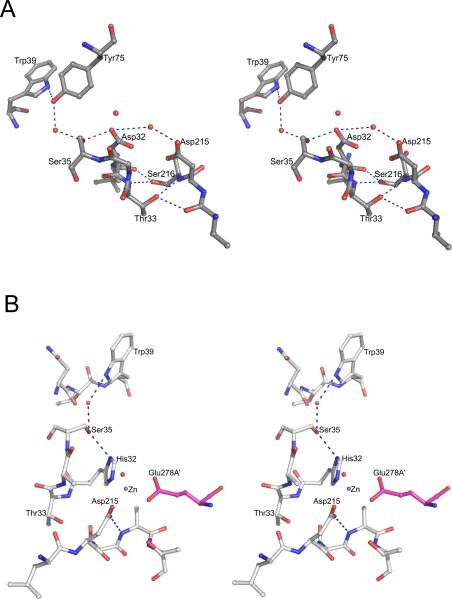
Figure 4.
The environment of the active sites of plasmepsins. (A) The active site of apo-PMII. Important water molecules are shown as red spheres. (B) One of the active sites of the apo-HAP dimer. The residues from one protomer are shown with carbons colored gray and Glu278A’ (from the other protomer, marked with a prime) is in magenta. Important water molecules are shown as red spheres. The bound Zn2+ ion is shown as a gray sphere.