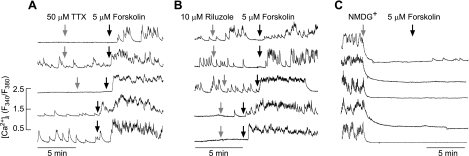
Fig. 5.
Sodium dependence of forskolin action on Ca2+ influx in rat anterior pituitary cells. A: stimulation of Ca2+ influx by 5 μM forskolin in cells bathed in 50 μM tetrodotoxin (TTX). Gray arrows indicate the moment of TTX application (top 3 traces). In some experiments, TTX was applied for 15 min prior to forskolin application (bottom 2 traces). B: the lack of effects of rilusole, a blocker of leak Na+ channels, on forskolin-stimulated Ca2+ influx. C: inhibition of spontaneous Ca2+ influx by replacing bath Na+ with N-methyl-d-glucamine (NMDG+). Notice the lack of effect of forskolin in cells bathed in NMDG+-containing medium. Traces shown are representative from 4 (A), 4 (B), and 3 experiments (C) with ≥15 recordings/experiment.