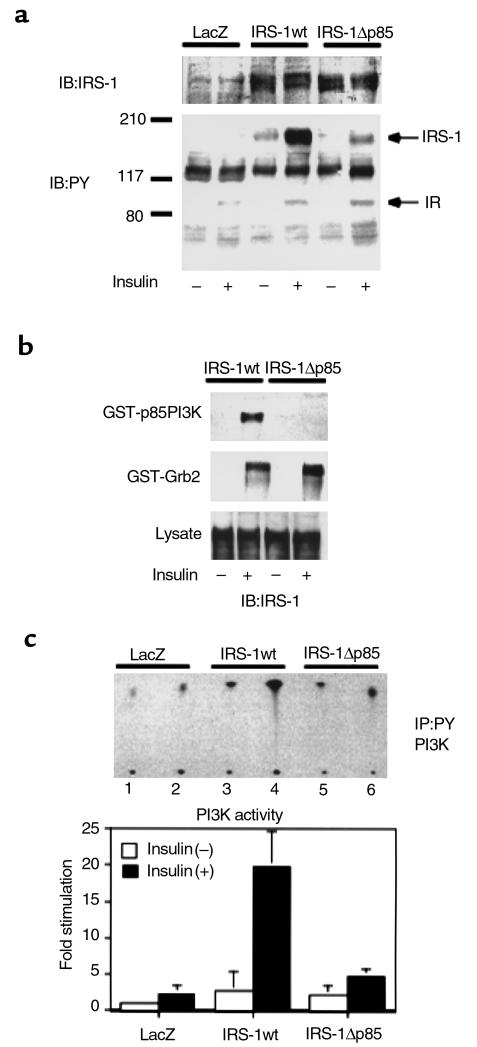
Figure 2.
Characterization of the IRS-1 mutant lacking p85 PI3K binding sites. (a) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the wild-type (IRS-1wt) or the mutant IRS-1 (IRS-1Δp85) in response to insulin. COS1 cells expressing human insulin receptors were infected with the indicated adenoviruses. After the infected cells were cultured in DMEM with 10% FCS for 48 hours, they were starved for 20 hours and treated with 100 nM insulin for 5 minutes. The cell lysates were subjected to Western blot (IB) with anti-IRS antibodies (upper panel) or anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies (lower panel). (b) The ability of the wild-type or the mutant IRS-1 to interact with SH2 proteins. After insulin treatment, the cell lysates were subjected to pull-down study using GST-p85PI3K fusion protein (upper panel) or GST-Grb2 fusion protein (lower panel) as described in Methods, followed by Western blot with αIRS-1CT. (c) The effect of IRS-1wt or IRS-1Δp85 expression on insulin-induced PI3K activity in COS1 cells. After insulin treatment, the cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies followed by PI3K assay as described in Methods. The upper panel shows the representative result (lanes 1, 3, and 5; insulin [–], lanes 2, 4, and 6; insulin[+]). In the lower panel, the results are expressed as the ratio to the value of wild-type without insulin, and each bar represents the mean ± SD of more than three independent experiments.