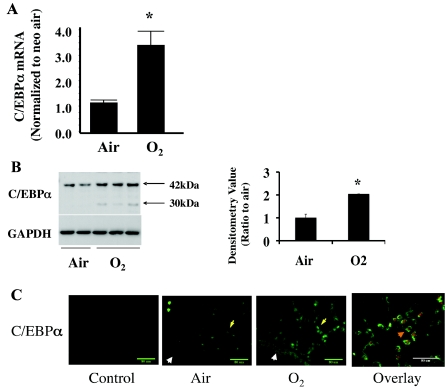
Fig. 1.
Hyperoxic induction of lung CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (C/EBPα) mRNA and its epithelial localization in neonatal (<12-h-old) mouse lung after 72 h of room air (Air) and 95% O2 (O2) exposure. A: C/EBPα mRNA increases in hyperoxia after normalization to room air. B: Western blots of C/EBPα immunoreactive protein levels (left) and densitometric evaluation of 42-kDa C/EBPα (right) in hyperoxia. Blots represent results from 4 experiments. Arrows indicate the 2 isoforms for C/EBPα protein. Values are means ± SE of 3 mice in each group. *P < 0.05 vs. Air. C: immunohistofluorescent staining of hyperoxia-induced C/EBPα in lung epithelial cells. Bronchiolar epithelial cells are indicated by white arrowheads and alveolar epithelial cells by yellow arrows. Overlay shows colocalization (orange arrowhead) of hyperoxia-induced C/EBPα (red staining) and ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 3 (ABCA3, green staining), a marker of alveolar type II cells.