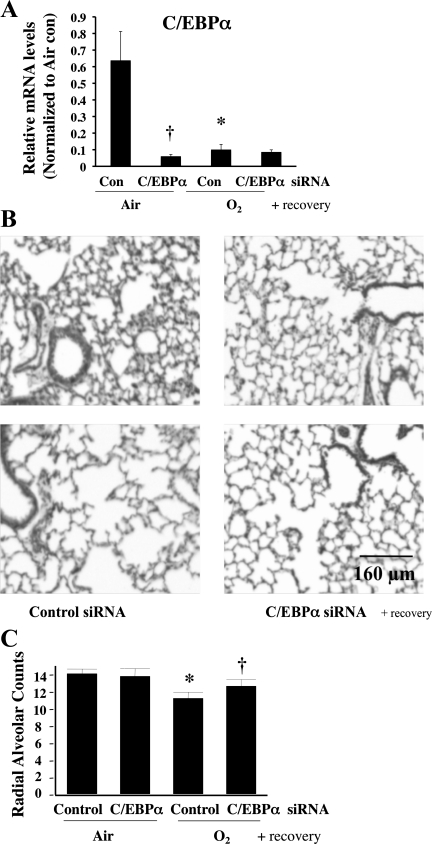
Fig. 5.
Effect of C/EBPα siRNA on lung architecture and RAC in lungs of neonatal mice exposed to hyperoxia and allowed to recover in room air. A: mRNA levels in C/EBPα siRNA-injected lung allowed to recover in room air. Values are means ± SE of 6 animals in each group. *P < 0.05 vs. control siRNA-injected lung (Con) in 72-h air exposure (Air). †P < 0.05 vs. C/EBPα siRNA-injected lung (C/EBPα siRNA) in Air. B: representative hematoxylin-eosin-stained lung sections. C: RAC in control (nonspecific) siRNA- and C/EBPα siRNA-injected lungs after room air recovery. Values are means ± SE of 5 animals in each group. *P < 0.05 vs. Control in Air. †P < 0.05 vs. Control in 72-h O2 exposure (O2).