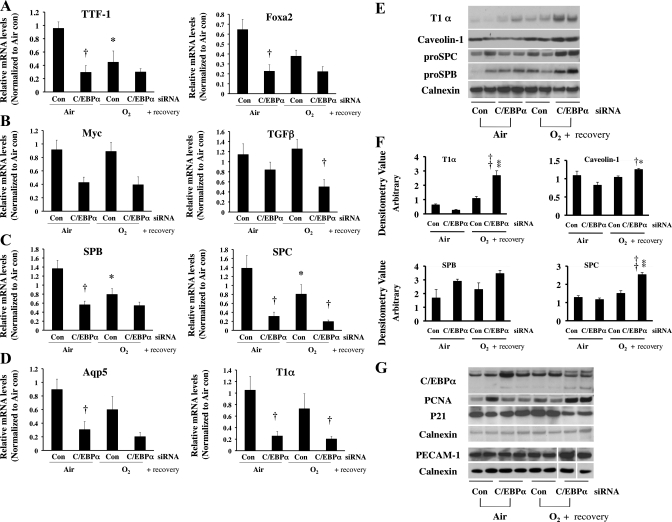
Fig. 6.
mRNA levels of TTF1 and FoxA2 as markers of lung development (A), myc and TGFβ as markers of cell differentiation (B), SP-B and SP-C as markers of type II cells (C), and aquaporin 5 and T1α as markers of type I cells (D) after intrapulmonary injection of C/EBPα siRNA into neonatal lung exposed to 72 h of hyperoxia (O2) and allowed to recover in room air. Values are means ± SE of 6 mice. *P < 0.05 vs. control siRNA-injected group (Con) in 72-h air exposure (Air). †P < 0.05 vs. C/EBPα siRNA-injected group (C/EBPα siRNA) in Air or O2. E: representative Western blots of type I (T1α and caveolin-1) and type II (pro-SP-C and pro-SP-B) cell marker proteins. F: densitometric evaluations of T1α, caveolin-1, pro-SP-B, and pro-SP-C protein levels from 6 lungs in each group. Values are means ± SE of 6 mice. *P < 0.05 vs. C/EBPα siRNA in Air. †P < 0.05 vs. Con in O2. **P < 0.001 vs. C/EBPα siRNA in Air. ††P < 0.001 vs. Con in O2. G: representative Western blots of protein levels of C/EBPα, PCNA (a general cell proliferation marker), p21 (a cell cycle inhibitor protein), and platelet/endothelial cell adhesion marker (PECAM-1, a vascular endothelial cell marker). In PECAM-1 immunoreactive protein evaluations, 3 lanes were omitted because of collapsed wells on acrylamide gel (white spaces). Each blot was normalized to corresponding calnexin protein levels to obviate loading variability.