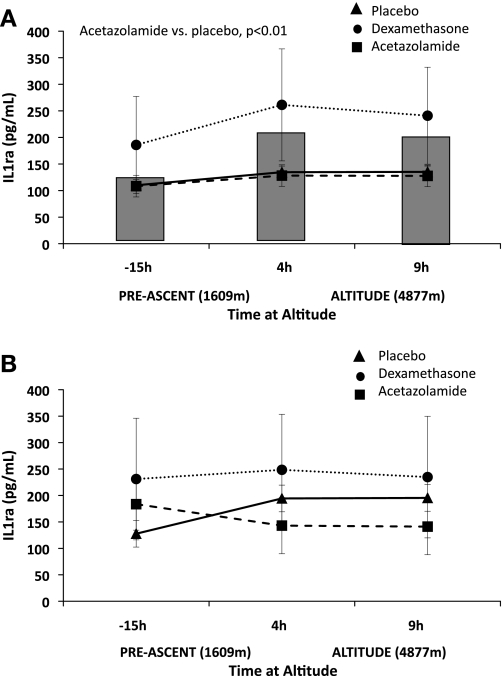
Fig. 1.
Comparison of acetazolamide and dexamethasone pretreatment on interleukin-1 receptor agonist (IL-1RA). Acetazolamide pretreatment increased IL-1RA compared with placebo in acute mountain sickness-susceptible subjects (AMS-S; P < 0.01; A), such that values were equivalent to the acute mountain sickness-resistant (AMS-R) group during hypoxia (P = nonsignificant; B). Dexamethasone had no effect in AMS-S. Neither drug influenced IL-1RA in AMS-R, with the exception of a tendency for dexamethasone to decrease IL-1RA relative to placebo at 4 and 9 h. The shaded bars behind the AMS-S figure (A) represent placebo IL-1RA values for AMS-R subjects to better visualize placebo comparisons between AMS-S and AMS-R subjects. Placebo, solid triangle with solid line; acetazolamide, solid circle, dotted line; dexamethasone, solid square, dashed line. Significant comparisons between placebo and drug pretreatment are designated in the figure by placebo vs. acetazolamide, or placebo vs. dexamethasone. Values are estimated marginal means ± SE.