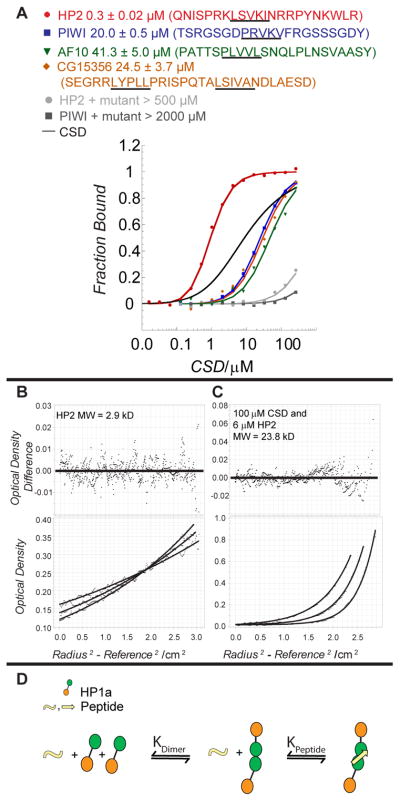
Figure 4. The HP2 peptide binds CSD dimers with high affinity.
A. Fluorescence polarization assays were used to determine the Kd for the binding of the HP2 peptide to wild-type HP1a-CSD and mutants W200A and I191E. The HP1a-CSD binding of the HP2 peptide is compared to PIWI, AF10, and CG15356 peptides, which have varying conservation of the PXVXL sequence motif. Data were fit as described in the Methods. Peptide sequences are listed above the plot and the critical pentapeptide motifs are underlined. The binding curves corresponding to HP2 compared to PIWI, CG15356, and AF10 exhibit a significant difference in Kd which brackets the modeled homodimerization binding curve of the CSD in the absence of peptide. The HP2 and PIWI peptides show no evidence of binding with the W200A mutant (binding curves shown); similar results were obtained with the I191E mutant. B&C. Determination of the molecular weight of the HP2 peptide alone (B) and of its complex (C) with the HP1a CSD by equilibration AUC demonstrates that 2 CSD molecules and 1 HP2 peptide form the complex. D. A model for HP1a dimerization and peptide association. The dissociation constants, KDimer and KPeptide are independent of each other. The high affinity of HP2 could drive dimerization of HP1a.