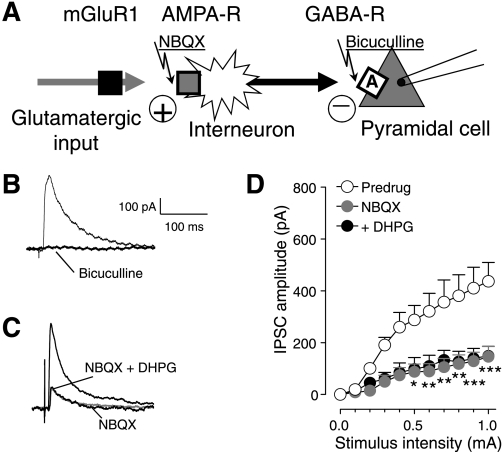
Fig. 4.
2,3-Dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide disodium salt (NBQX) blocks the facilitatory effect of DHPG on inhibitory synaptic transmission. Whole cell voltage-clamp recordings of visually identified prelimbic layer V pyramidal cells. A: diagram illustrates our hypothesis that DHPG (through metabotropic glutamate receptor 1, mGluR1) activates feed-forward inhibition of medial PFC cells through a mechanism that involves non-N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) (3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole propionic acid, AMPA) and GABAA receptors. Squares indicate receptors. B: individual traces (averages of 8–10 IPSCs recorded at 0 mV) show that IPSCs were blocked by a GABAA receptor antagonist (bicuculline, 10 μM). C: individual traces (averages of 8–10 IPSCs) show that IPSCs were inhibited by a non-NMDA (AMPA) receptor antagonist (NBQX, 10 μM). DHPG (1 μM) coapplied with NBQX had no effect. D: NBQX inhibited GABAergic IPSCs significantly (n = 5, 2-way ANOVA, F1,88 = 80.14, P < 0.0001) and blocked the effect of DHPG (n = 5, 2-way ANOVA, F1,88 = 0.95, P > 0.05, compared with NBQX alone). Symbols show means ± SE. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.