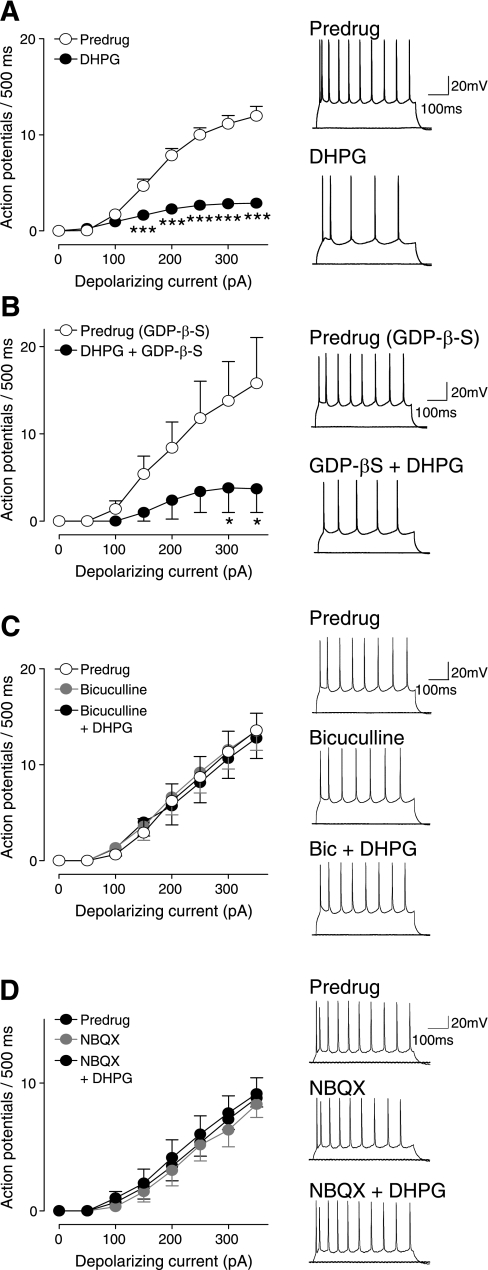
Fig. 7.
DHPG-induced synaptic inhibition inhibits pyramidal output (depolarization-induced spiking). Whole cell current-clamp recordings of visually identified prelimbic layer V pyramidal cells. Action potentials were generated by direct intracellular current injections (500 ms) of increasing magnitude (in 50-pA steps) from a holding potential of −60 mV. Right: original voltage traces showing action potentials evoked in individual cells by current injections of 0 pA and 300 pA. Left: graphs showing input-output functions (f-I relationships) averaged for each sample of neurons. A: DHPG (1 μM) decreased the input-output function significantly (n = 28 neurons, 2-way ANOVA, F1,432 = 257.01, P < 0.0001). ***P < 0.001 (Bonferroni posttests). B: when GDP-β-S (1 mM) was included in the patch pipette (predrug), DHPG still had inhibitory effects (n = 5 neurons, 2-way ANOVA, F1,64 = 16.84, P < 0.001). *P < 0.05 (Bonferroni posttests). C: bicuculline (10 μM) itself did not affect neuronal excitability but blocked the inhibitory effect of DHPG (n = 7 neurons, 2-way ANOVA, F1,96 = 0.28, P > 0.05). D: NBQX (10 μM) also had no effect on action potential firing but blocked the effect of DHPG (n = 6, 2-way ANOVA, F1,80 = 0.57, P > 0.05). Symbols show means ± SE.