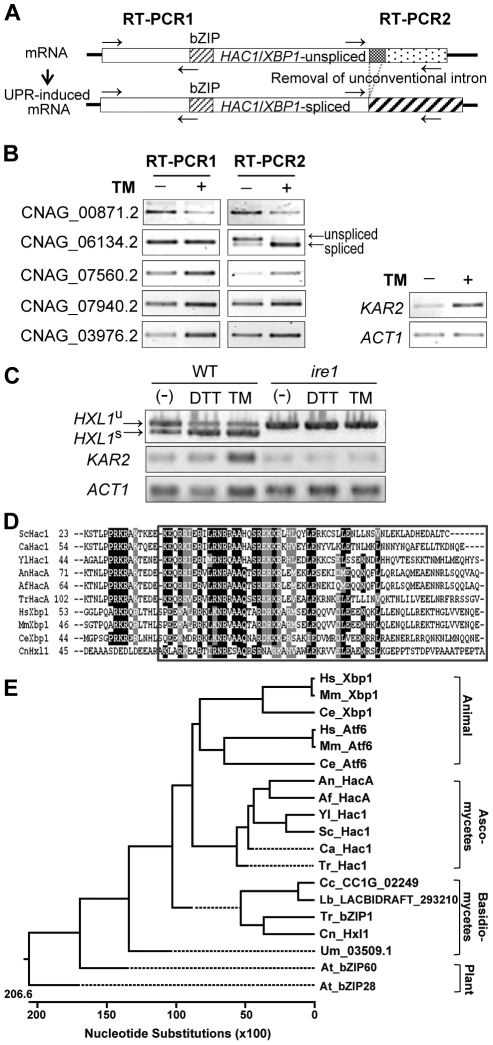
Figure 2. Identification of a novel Ire1-dependent bZIP transcription factor, Hxl1, in C. neoformans.
(A) General mRNA structures of the unspliced and spliced HAC1/XBP1. For identification of putative HAC1/XBP1 homologs, primers for RT-PCR1 and RT-PCR2 were designed to amplify the 5′-region product and the unconventionally spliced 3′-region product, respectively. (B) RT-PCR analysis for testing UPR-induced splicing. RT-PCR of CNAG_00871.2, CNAG_06134.2, CNAG_07560.2, CNAG_07940.2, CNAG_03976.2, KAR2 (CNAG_06443.2), and ACT1 (CNAG_00483.2) were performed with the cDNA samples of H99 strain cultivated in YPD medium with or without TM (5 µg/ml) treatment for 1 hr. (C) IRE1-dependent splicing of CNAG_06134.2. Strains were cultivated in YPD with or without TM (8 µg/ml) or DTT (20 mM). (D) Alignment of bZIP domains observed in Hxl1 and Hac1/Xbp1 homologs from several fungi and mammals. DNA binding domain of the bZIP domain is boxed. (E) Phylogenetic tree of the bZIP domains of transcription factors responsible for ER stress responses or Hxl1 homologs in fungi (ascomycete and basidiomycete), worm, plant, and animals. Hs: Homo sapiens Xbp1 (NP_001073007), Atf6 (NP_031374); Mm: Mus musculus Xbp1 (AAL60202), Atf6 (NP_001074773); Ce: Caenorhabditis. elegans Xbp1 (AAL60201), Atf6 (NP_510094); Sc, S. cerevisiae Hac1 (NP_116622); Ca: C. albicans Hac1 (EF655649); Yl: Yarrowia lipolytica Hac1 (XP_500811); An: Aspergillus nidulans hacA, Q8TFU8; Af: A. fumigatus HacA, ACJ61678; Tr: T. reesei hac1 (Q8TFF3); Cn: C. neoformans Hxl1 (CNAG_06134.2); Um: Ustilago maydis UM03509.1; Tf: Tremella fuciformis bZIP 1 (XP_001877531); Lb: Laccaria bicolor LACBIDRAFT_293210; Cc: Coprinopsis cinerea CC1G_02249; At: Arabidopsis thaliana bZIP28 (NP_187691), bZIP60 (NP_174998).