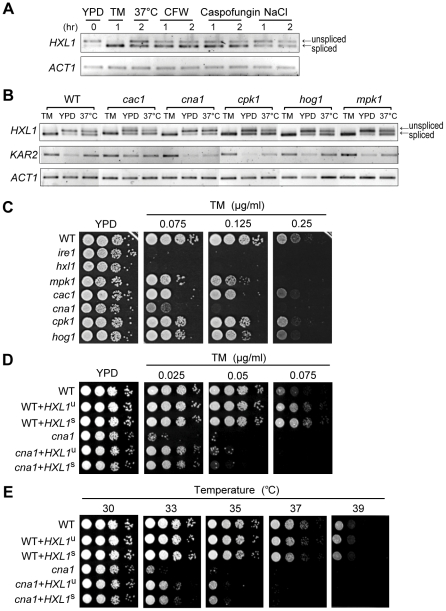
Figure 9. Induction of the UPR pathway by other stresses and potential crosstalk with other signaling pathways.
(A) Analysis of the HXL1 splicing pattern during cell wall and osmotic stresses. RT-PCR of HXL1 and ACT1 were performed with the cDNA samples of H99 strain untreated or treated with TM (5 µg/ml), CFW (20 mg/ml), caspofungin (6 µg/ml), and NaCl (1 M) at 30°C, or at 37°C, respectively, for the indicated times. (B) Analysis of the HXL1 expression pattern in signaling mutants under ER or heat stress conditions. RT-PCR of HXL1, KAR2, and ACT1 was performed with cDNA samples of strain H99 untreated or treated with 5 µg/ml TM for 1 hr at 30°C, or at 37°C for 2 hr, respectively. (C) Analysis of ER-stress sensitivity of various signaling mutants. Strains were spotted serially and incubated on YPD media with or without indicated concentrations of TM at 30°C for 2.5 days. (D and E) Phenotypic analyses of WT (H99) and cna1 mutant strains having increased expression of HXL1 against TM and thermotolerance. Each strain [WT, WT+HXL1 u (YSB736), WT+HXL1 s (YSB741), cna1, cna1+HXL1 u (YSB1320), and cna1+HXL1 s (YSB1325)] was spotted on YPD medium with indicated concentrations of TM and incubated at 30°C for 3 days for TM sensitivity or was incubated on YPD medium at indicated temperatures for 3 days for thermotolerance test.