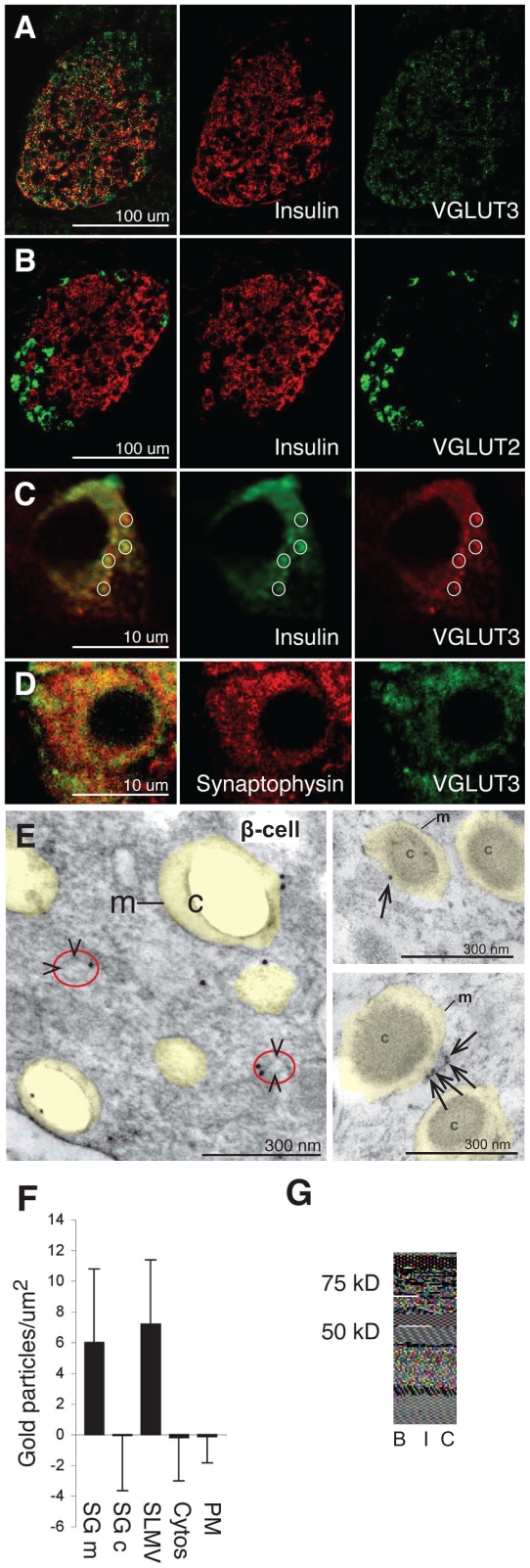
Figure 1. The vesicular glutamate transporter VGLUT3 is localized in secretory granules and synaptic-like microvesicles (SLMVs) in pancreatic β-cells.
(A) VGLUT3 (green) co-localizes with insulin (red), but is also found in peripheral non-B islet cells. (B) VGLUT2 (green) does not co-localize with insulin (red). (C) A single β-cell from the islet presented in panel A: VGLUT3 (red) co-localizes partly with insulin (green). The circles highlight some of the overlapping VGLUT3 and insulin dots. (D) A single β-cell: VGLUT3 (green) co-localizes partly with synaptophysin (red) in small dots. (E) Electron micrograph showing immunogold particles for VGLUT3 in two β-cells. Secretory granules are indicated by transparent yellow. m, membranes of secretory granules. c, core of the secretory granule (of which some disappeared in the preparation procedure). SLMVs are indicated by arrowheads and red circles. (F) Quantification of VGLUT3 in β-cells (n = 8 cells). Immunogold particle densities (mean number of gold particles/µm2 ±SD) in the membrane of the granules (SGm) and in SLMVs are significantly higher than in the core of the β-cell granules (SGc), cytosol and plasma membranes (PM) (background labeling, quantified over mitochondria, is subtracted, see Methods) (p<0.001, Mann-Whitney-U test, two tails). (G) Western blots of rat brain tissue (B) and isolated rat islets (I) probing for VGLUT3. (C), islet blot without the VGLUT3 primary antibodies.