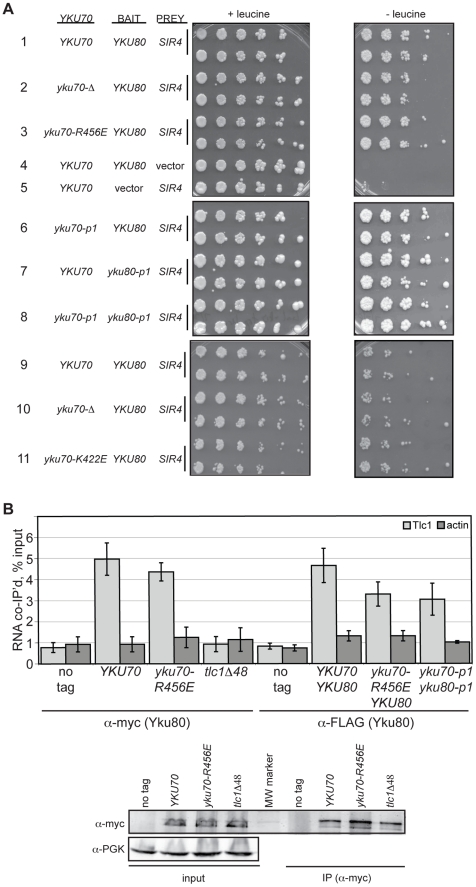
Figure 3. DNA end binding–defective Ku heterodimers interact with Sir4 and TLC1.
(A) Yku80-Sir4 yeast-two-hybrid assay. YAB327 was transformed with indicated YKU70 plasmid, a BAIT plasmid (YKU80, vector, or yku80-p1) and the PREY (SIR4 or vector) plasmid. Serial dilutions of these strains were plated onto –His –Trp –Ura in the presence (+) or absence (–) of leucine. Interaction between Yku80 and Sir4 results in activation of a LEU2 reporter and growth in the absence of leucine. (B) TLC1 co-immunoprecipitation. WCEs were prepared from strains with the indicated genotypes, α-myc or α-FLAG immunoprecipitations performed, RNA isolated, and TLC1 and actin RNA analyzed by reverse transcriptase RT-PCR. Reverse transcriptase RT-PCR was also carried out on WCEs prior to immunoprecipitation to control for RNA levels and calculate percent RNA co-immunoprecipitated. A bar graph shows the amount of TLC1 co-immunoprecipitated with myc- or FLAG-tagged Yku80. Error bars represent one standard deviation (SD). α-Myc western blot showing equal IP of myc-tagged Yku80 in YKU70, yku70-R456E, and tlc1-Δ48 strains. α-PGK serves as a control for protein levels for the input WCEs prior to immunoprecipitation.