Figure 6.
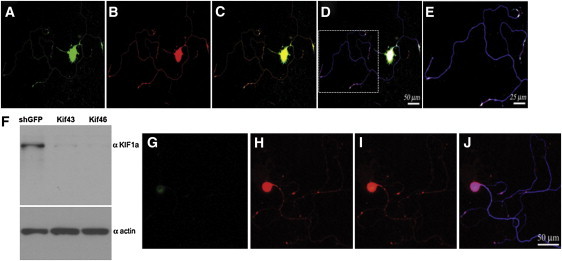
Localization of KIF1A and WNK1/HSN2 and Silencing of KIF1A in Adult Mouse DRG Neurons
(A–E) Sequential laser confocal scans to compare the localization of KIF1A and WNK1/HSN2. Neurons were cultured 48 hr prior to their immunodetection. KIF1A and WNK1/HSN2 colocalize well, as evidenced by the use of anti-KIF1A (A, green), anti-HSN2 (B, red) and anti-betaIII tubulin (blue).
(C) Merged image of (A) and (B); strong colocalization of green and red is yellow.
(D) Merged image of (C) and the matching betaIII tubulin detection; strong colocalization of red and blue is pink.
(E) Enlargement of the boxed image area in (D).
(F–J) Lentiviral shRNA-mediated knockdown of KIF1A. Twenty-four hours after their plating, primary neurons were infected overnight with lentiviral particles expressing shRNA (kif46) so that KIF1A would be silenced. (F) Immunoblot analysis confirmed the knockdown of KIF1A in neurons infected by lentivirus expressing shRNA against KIF1A (Kif43 and Kif46). Control lysates were prepared from cells infected with lentiviruses expressing shRNA against GFP, and an actin antibody showed equal loadings. Cells were grown for 4 days after infection before their immunodetection with anti-KIF1A (G, green), anti-HSN2 (H, red), and anti-betaIII tubulin. (I) Merged image of (G) and (H). (J) Merged image of (I) and the matching betaIII tubulin detection (blue).
