Fig. 1.
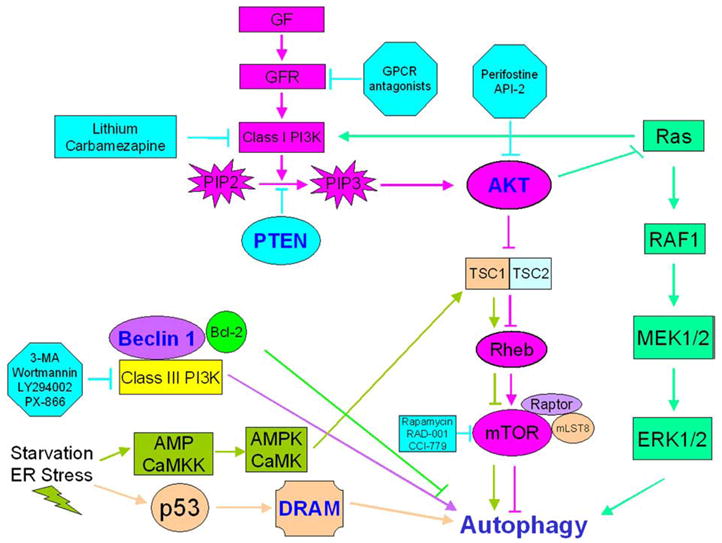
Autophagy regulation. Growth factor signaling activates the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis resulting in autophagy inhibition. Consequently, G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) antagonists inhibiting growth factor receptors, lithium and carbamazepine negatively regulating class I PI3K, perifostine and AKT/PKB signaling inhibitor-2 (API-2) downregulating AKT activation, and rapamycin, RAD001 and CCI-779 inhibiting mTOR play pivotal roles in autophagy upregulation. In contrast, class III PI3K activates autophagy, and thus class III PI3K inhibitors such as 3-MA, wortmannin, LY294002 or PX-866 suppress autophagy. At least two pathways are responsible for autophagy activation in response to starvation and ER stress: one mediated by AMPK and CaMKK, and the other involving p53 and damage-regulated autophagy modulator (DRAM) activation. In this complex regulatory network, Ras exhibits dual function as both an autophagy inhibitor (via class I PI3K activation) and an autophagy activator (via the RAF1/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 pathway).
