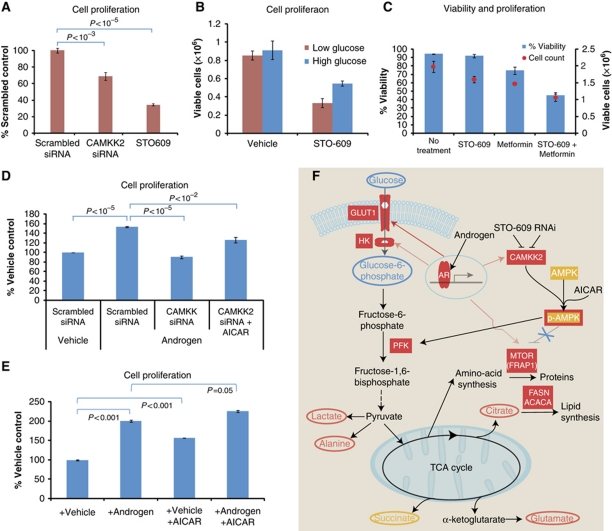
Figure 5.
AR-CAMKK2-AMPK signalling is required for AR-stimulated proliferation in prostate cancer cells. (A) Cell proliferation of LNCaP cells 120 h following CAMKK2 siRNA transfection or CAMKK2 inhibitor treatment (25 μM STO-609; represented as % no treatment control, average of triplicate MTS assay experiments±s.e.m.). (B) Viable cell counts 72 h following treatment of LNCaP cells with CAMKK2 inhibitor (25 μM STO-609), in low glucose medium (1 g/l) or high glucose medium (4.5 g/l; represented as average of triplicate experiments±s.e.m.). (C) Viable cell counts and percentage viability of LNCaP cells following 72 h treatment with CAMKK2 inhibitor (25 μM STO-609), the anti-diabetes drug metformin (5 mM) or the combination treatment (average of triplicate experiments±s.e.m.). (D) Cell proliferation of LNCaP cells cultured in steroid depleted medium for 120 h following transfection with scrambled siRNA or CAMKK2 siRNA, with or without androgen stimulation (1 nM R1881) or AMPK activation (200 μM AICAR; average of triplicate MTS experiments±s.e.m.). (E) Cell proliferation of LNCaP cells cultured in steroid depleted medium for 120 h and treated with vehicle (0.01% ethanol) or androgen (1 nM R1881) with or without AMPK stimulation (200 μM AICAR; average of triplicate MTS experiments±s.e.m.). (F) Schematic model of AR-CAMKK2 signalling in prostate cancer cells, highlighting the pathways implicated in the stimulation of glycolysis, biosynthesis and proliferation via AMPK (upstream metabolites indicated in blue ovals, downstream metabolites indicated in red ovals and AR-regulated genes indicated by solid red boxes, yellow indicates metabolites and genes showing no detected change).