Abstract
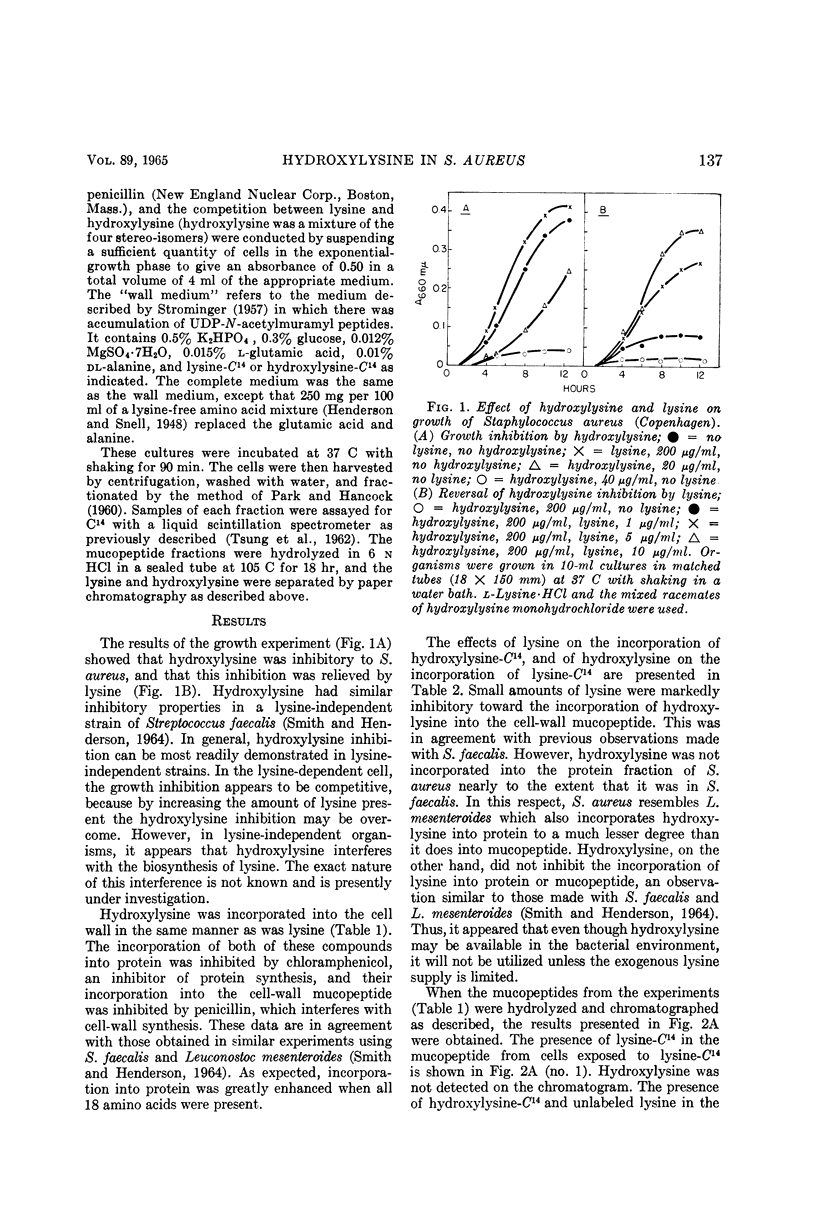
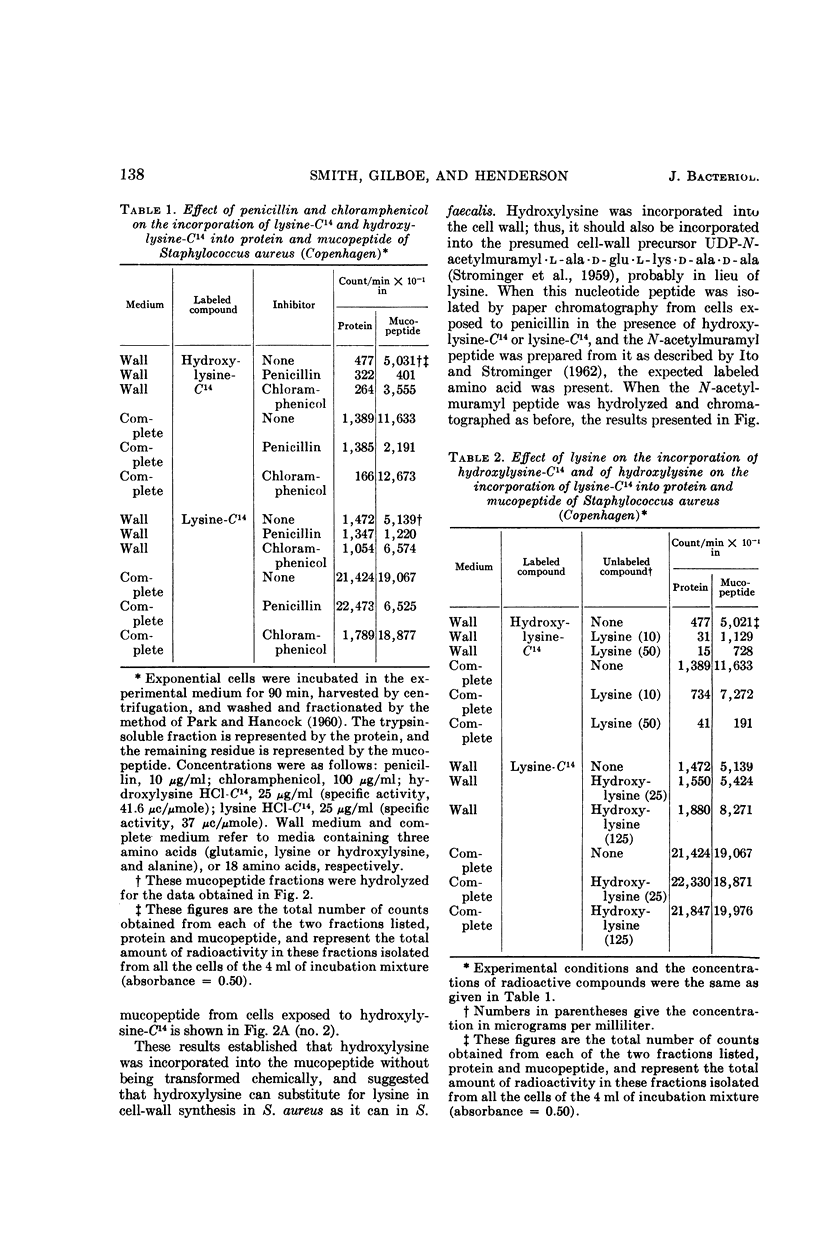
Smith, W. Grady (University of Minnesota, St. Paul), Daniel P. Gilboe, and L. M. Henderson. Incorporation of hydroxylysine into the cell wall and a cell-wall precursor in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 89:136–140. 1965.—Recent work has shown that hydroxylysine can substitute for lysine in cell-wall synthesis of Streptococcus faecalis, apparently becoming incorporated into cell-wall mucopeptide. This paper extends these observations to investigate the metabolism of hydroxylysine in Staphylococcus aureus, an organism from which sufficiently large quantities of cell-wall precursors. uridine diphosphate-N-acetylmuramyl peptides, could be obtained. Hydroxylysine has been shown to be incorporated into the cell-wall precursor uridine diphosphate-N-acetylmuramyl l-ala·d-glu· l-lys·d-ala·d-ala from S. aureus (Copenhagen) apparently in lieu of lysine. Hydroxylysine was also incorporated into the cell-wall mucopeptides of S. aureus in resting cultures. This incorporation was inhibited by penicillin or lysine, but not by chloramphenicol. Hydroxylysine had little effect on the incorporation of lysine into S. aureus. Hydroxylysine acted as a growth inhibitor in this organism; the inhibition was reversed by lysine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHATTERJEE A. N., PARK J. T. BIOSYNTHESIS OF CELL WALL MUCOPEPTIDE BY A PARTICULATE FRACTION FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:9–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J., ROGERS H. J. The incorporation of amino acids into the cell-wall mucopeptide of staphylococci and the effect of antibiotics on the process. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:654–662. doi: 10.1042/bj0720654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow P. M., Anderson J. S., Strominger J. L. Enzymatic polymerization of UDP-acetylmuramyl.L-ala.D-glu.L-lys.D-ala.D-ala and UDP-acetylglucosamine by a particulate enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus and its inhibition by antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:382–387. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T. Uridine-5'-pyrophosphate derivatives. II. Isolation from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):877–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH W. G., HENDERSON L. M. RELATIONSHIPS OF LYSINE AND HYDROXYLYSINE IN STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS AND LEUCONOSTOC MESENTEROIDES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1867–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH W. G., NEWMAN M., LEACH F. R., HENDERSON L. M. The effect of hydroxylysine on cell wall synthesis and cell stability in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1198–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNELL E. E., RADIN N. S., IKAWA M. The nature of D-alanine in lactic acid bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):803–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L. Microbial uridine-5'-pyrophosphate N-acetylamino sugar compounds. I. Biology of the penicillin-induced accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jan;224(1):509–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUNG C. M., SMITH W. G., LEACH F. R., HENDERSON L. M. Hydroxylysine metabolism in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1194–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney J. G., Grula E. A. Incorporation of D-serine into the cell wall mucopeptide of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:375–381. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


