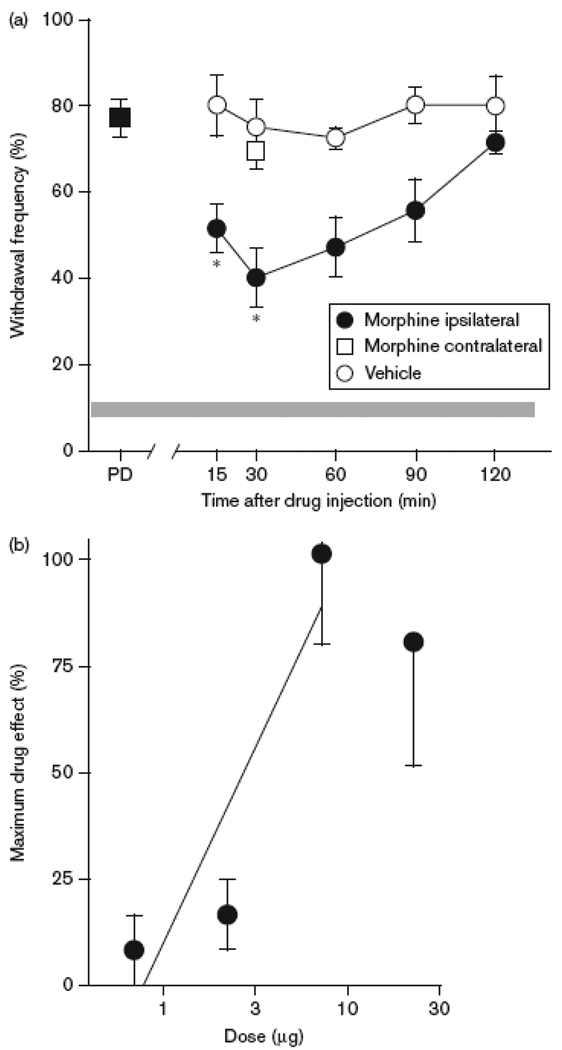
Figure 6.
Morphine attenuated tumor-evoked mechanical hyperalgesia. A. Time course of the anti-hyperalgesic effect of morphine (7 µg, i.pl.). A reduction in mechanical hyperalgesia occurred at the earliest time point measured (15 min) and persisted through 1.5 h. *Different from vehicle at respective time point at p<0.01 (n=6–7 mice/group; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s analysis). Intraplantar injection of morphine contralateral to the tumor did not modulate hyperalgesia in the tumor-bearing paw (□). B. The anti-hyperalgesic effect of morphine was dose-dependent with an ED50 of 2.92 µg (95% CI: 1.9 to 5.4 µg). Dose was plotted on a log scale.