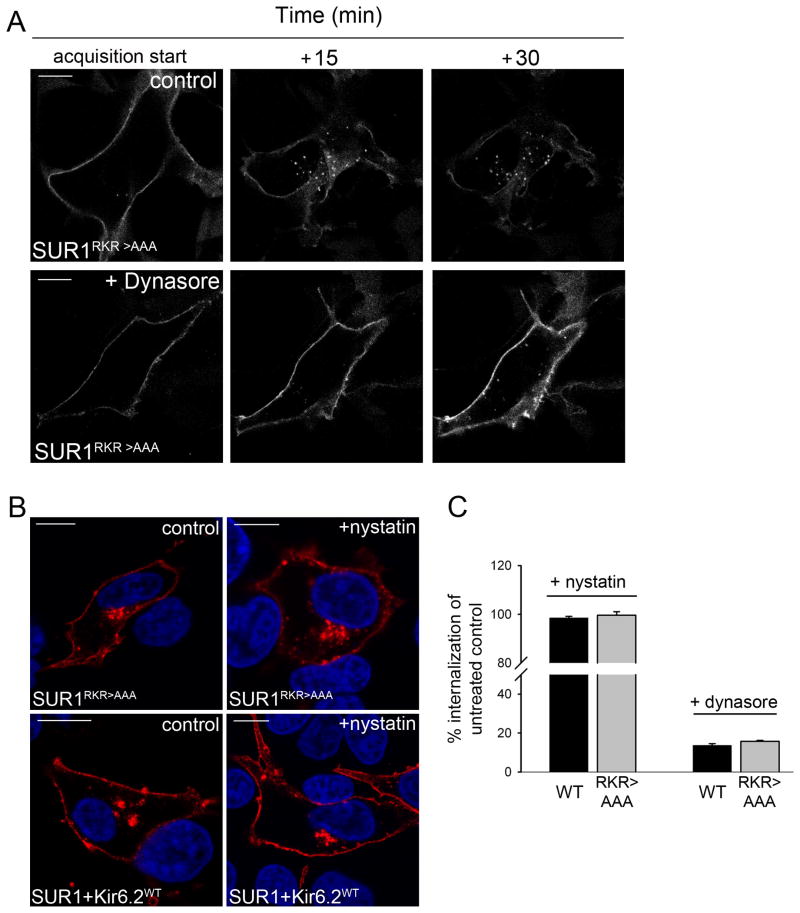
Figure 6. SUR1RKR→AAA endocytosis is dynamin-dependent but not caveolae-mediated.
(A) Endocytosis of cells expressing BTX tag-SUR1RKR→AAA was monitored by live cell imaging either with or without dynasore treatment, a potent inhibitor of the large GTPase dynamin that is involved in clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Control cells not treated with dynasore showed robust internalization of SUR1RKR→AAA over a 30min time interval (top, scale bar 10μm) while endocytosis of SUR1RKR→AAA was almost completely blocked when the cells were treated with dynasore (bottom, scale bar 10μm) and the protein accumulated at the plasma membrane due to decreased endocytosis (see bright fluorescent surface staining at 30min in dynasore treated cell), indicating that SUR1RKR→AAA internalization is dynamin dependent (movies in supplemental material). (B) To test whether SUR1RKR→AAA internalization is mediated by caveolae cells were incubated with 25μg/ml nystatin, an inhibitor of caveolae-mediated endocytosis, labeled with TRITC-BTX dye at 4°C and chased for 30min at 37°C. SUR1RKR→AAA showed robust internalization when treated with nystatin comparable to untreated control cells (B, upper panel, all scale bars 10μm). The same observations were made in cells expressing WT channels (B, lower panel) indicating that neither SUR1RKR→AAA nor WT channel endocytosis is caveolae-mediated. (C) Quantitative analysis of endocytosis in nystatin and dynasore treated cells. Internalization of channels was measured as average intracellular fluorescence intensity present after 30min of chase. When treated with nystatin, cells expressing WT or SUR1RKR→AAA showed internalization rates comparable to untreated controls (n=4/condition).