Figure 3.
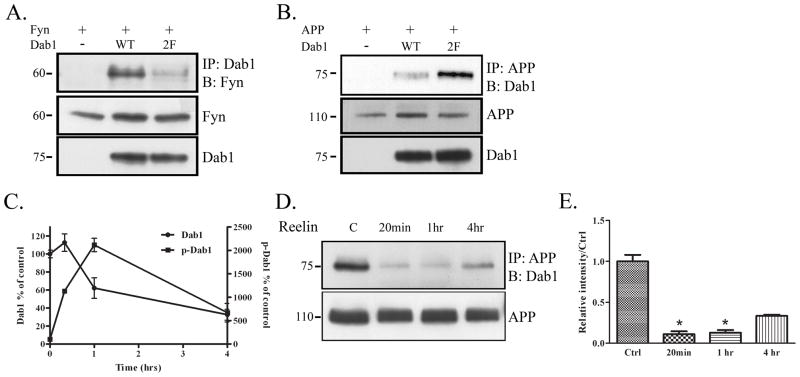
Phosphorylation of Dab1 decreases interaction with APP. A. COS7 cells were transfected with Fyn and vector, Dab1 WT, or a Dab1 construct that contained phenylalanine substitutions at two of its tyrosine residues, Dab1(2F). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Dab1 and blotted for Fyn (top panel). Dab1(2F) co-precipitated with Fyn less compared to Dab1 WT. Levels of Fyn and Dab1 remained constant (bottom panels). B. COS7 cells were transfected with APP and empty vector, Dab1 wild-type construct, or Dab1(2F). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with APP and blotted for Dab1 (top panel). Dab1(2F) co-precipitated more with APP compared to Dab1 WT. Levels of APP and Dab1 remained constant (bottom panels). C. Primary neurons from wild-type mice (DIV14) were treated with Reelin for 20 min, 1 hr, or 4 hrs. Cell lysates were collected and blotted for Dab1, or immunoprecipitated with phosphotyrosine and blotted for Dab1. Blots of 3 independent experiments were quantified and represented in the graph shown. Total Dab1 decreased over time after 1 hr of Reelin treatment (left axis). Phosphorylated Dab1 increased over time until 1 hr of Reelin treatment (right axis). D. Primary neuronal lysates from the Reelin treatment were immunoprecipitated with APP and blotted for Dab1 (top panel). Co-precipitation between APP and Dab1 decreased with 20 min of Reelin treatment, stayed low at 1 hr, and recovered partially at 4 hrs. Total levels of APP remained constant over time (bottom panel). E. Quantification of data in D (n=2) shows an 89% decrease in APP-Dab1 interaction compared to control at 20 min (p<0.05), an 87% decrease at 1 hr (p<0.05), and a 67% at 4 hrs (p=0.07) of Reelin treatment (by student’s t-test with unequal variance).