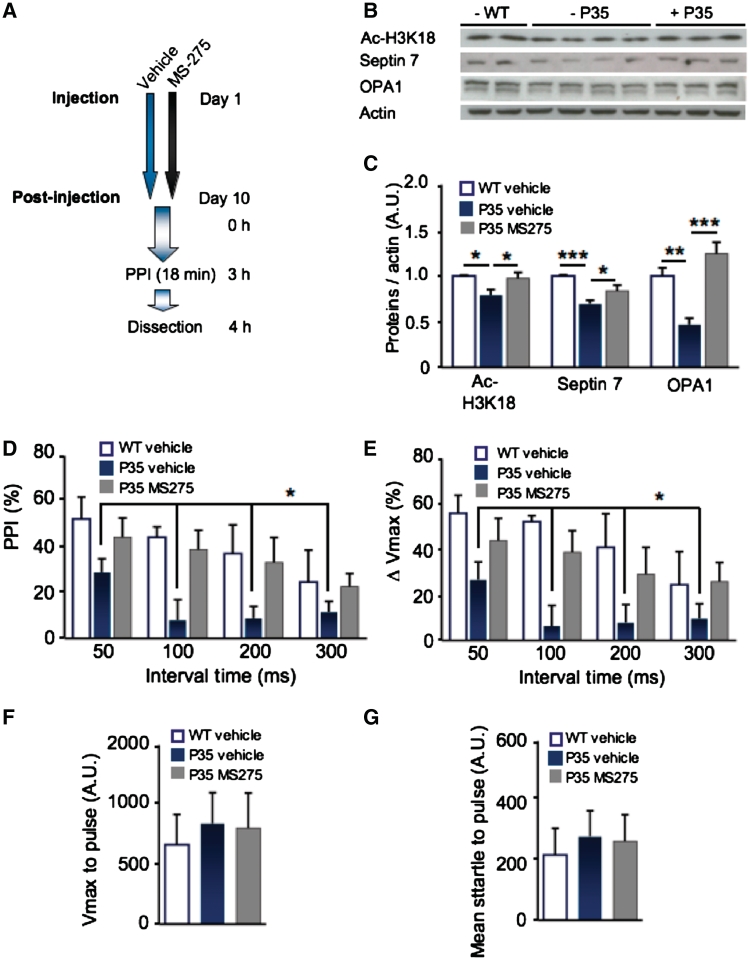
Figure 6.
Administration of MS-275 rescues molecular endophenotypes and prepulse inhibition in female p35+/− mice. (A–G) p35+/− mice and wild-type (WT) littermates were injected intraperitoneally for 10 days with either the HDAC1-inhibitor MS-275 or vehicle. (A) Scheme of the experiment. (B and C) Total hippocampal lysates were western blotted against acetyl-H3K18, septin 7 and OPA1. (C) There was a significant reduction in expression of septin 7 and OPA1 and H3K18 acetylation in p35 mutants, which was rescued by administration of MS-275. (D and E) Prepulse inhibition (PPI) was tested with a protocol comprising four different interval times. Weight was analysed as covariate as weight correlated with detected startle amplitudes and therefore affected the measurements. There was a significant treatment by genotype interaction for the prepulse inhibition as measured by change in the mean (ΔPPI) and the maximum (ΔVmax) startle amplitudes. Post hoc analysis revealed that this change arises from reduced prepulse inhibition in female p35+/− mice in the vehicle group as well as from an effect of drug treatment within p35 mutants and within wild-type mice. (F and G) The baseline startle response was not affected by administration of MS-275 [− = vehicle; + = MS-275; n = 4–8 per group; (D and E) asterisks represent sex by genotype interaction and post hoc data; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; average ± SEM shown].