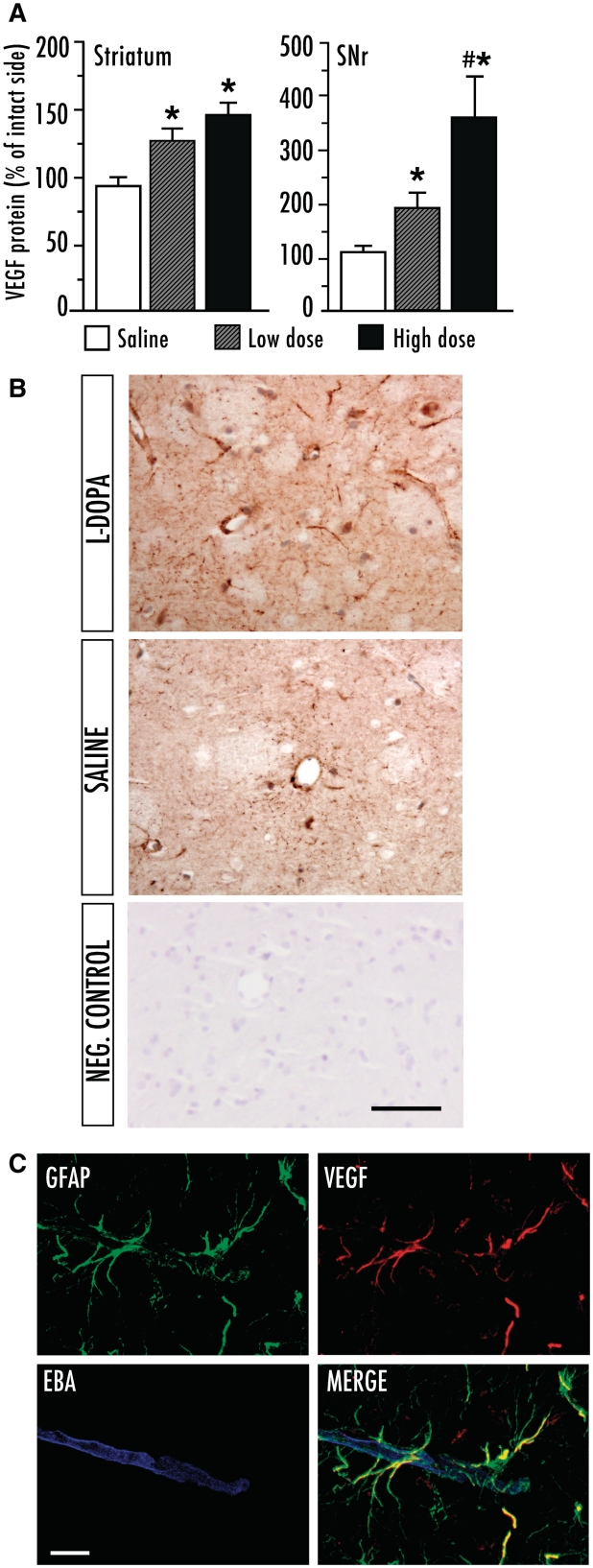
Figure 4.
Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are dose-dependently upregulated in the basal ganglia following chronic l-dopa treatment. (A) VEGF protein levels (measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) in the striatum and substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr). l-Dopa high dose (n = 6), l-dopa low dose (n = 6), saline (n = 10). Results from the l-dopa-denervated hemisphere are expressed as a percentage of the intact side in each subject to normalize for inter-assay variability. One-factor ANOVA followed by post hoc Student–Newman–Keul’s; P < 0.05 *versus saline, #versus low dose. (B) Bright-field VEGF immunohistochemistry on striatal sections from l-dopa and saline-treated rats. The negative control was obtained by pre-absorbing the primary antiserum with a 5-fold larger concentration of the immunizing peptide (the section was lightly counterstained with Mayer’s haematoxylin to visualize the tissue). (C) Laser scanning confocal microscopy of triple immunofluorescence for glial fibrillary astrocytic protein (GFAP), VEGF and endothelial barrier antigen (EBA). Endothelial barrier antigen was used as an endothelial marker, and areas of reduced immunopositivity could be seen in proximity of the VEGF-positive astrocytes. Scale bar = 50 μm (B) and 10 μm (C).