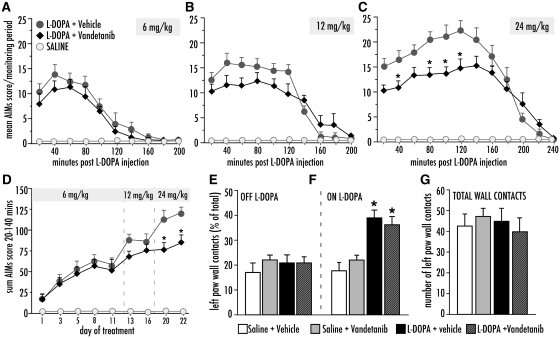
Figure 6.
Co-treatment with Vandetanib attenuated the development of abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) upon chronic treatment with l-DOPA. Rats were treated with l-DOPA at increasing doses (day 1–12, 6 mg/kg; day 13–19, 12 mg/kg; day 20–22, 24 mg/kg). (A) Development of AIMs following one l-DOPA injection at the low-dose treatment (6 mg/kg), (B) medium dose treatment (12 mg/kg), and (C) high dose treatment (24 mg/kg). l-DOPA+ vehicle (n = 12), l-DOPA+ Vandetanib (n = 10), saline (n = 12). (D) Global AIMs scores after each dose and test. Repeated measures ANOVA (in C and D), followed by Tukey's HSD post hoc comparisons where appropriate. P < 0.05, *versus l-DOPA + vehicle. (E–G) Cylinder test of forelimb use asymmetry showed no difference between the groups treated with Vandetanib or vehicle treated groups. (E) Performance measured ‘OFF’ l-DOPA (day 12) or (F) Performance ‘ON’ l-DOPA (90 minutes post L-DOPA injection), (G) total activity (total touches against cylinder wall). One-factor ANOVA followed by post hoc Student-Newman Keul's. Values expressed as mean S.E.M. *P < 0.05 versus saline-treated groups.