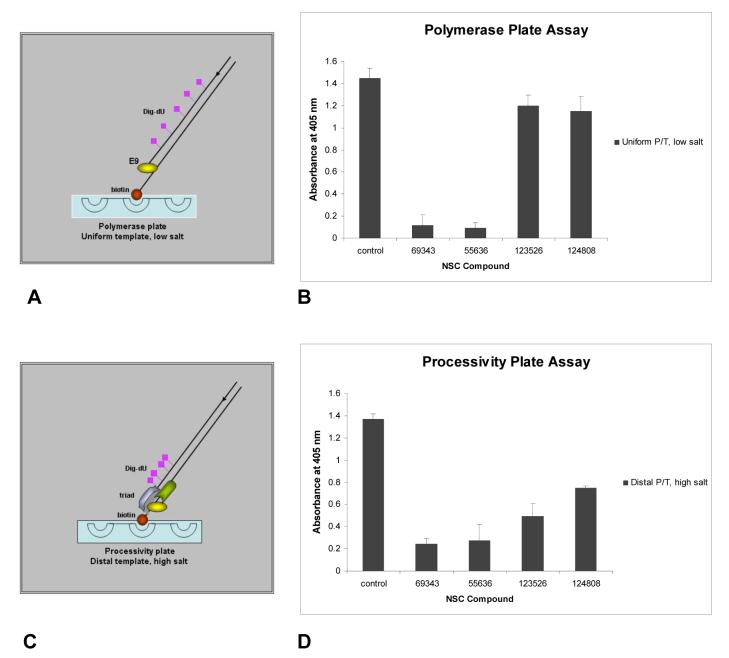
Figure 4.
Assay to distinguish polymerase and processive inhibitors of vaccinia DNA synthesis. (A) The model depicts the uniform incorporation of the DIG-dU on a template by E9 polymerase under low salt conditions. Under low salt conditions, E9 incorporates dNTPs along the DNA template. (B) NCI hit compounds were analyzed on the uniform tempate in the presence of E9 alone under low salt conditions to identify polymerase inhibitors. (C) The model depicts incorporation of the label DIG-dUTP on the distal end of the template by the triad (A20, D4, E9) under high salt conditions. This template was designed with all the adenines near the biotinylated end to direct incorporation of the DIG label towards the 3′ of the growing strand. Under high salt conditions, E9 requires A20 and D4 to accomplish processive DNA synthesis. (D) NCI hit compounds were analyzed on the distal tempate in the presence of the A20, D4 and E9 triad under high salt conditions to identify processivity inhibitors. Compounds that block E9 polymerase activity also blocked processivity. For both A and C, the template 5′ end is biotinylated for attachment to the streptavidin-coated plates.