Figure 1.
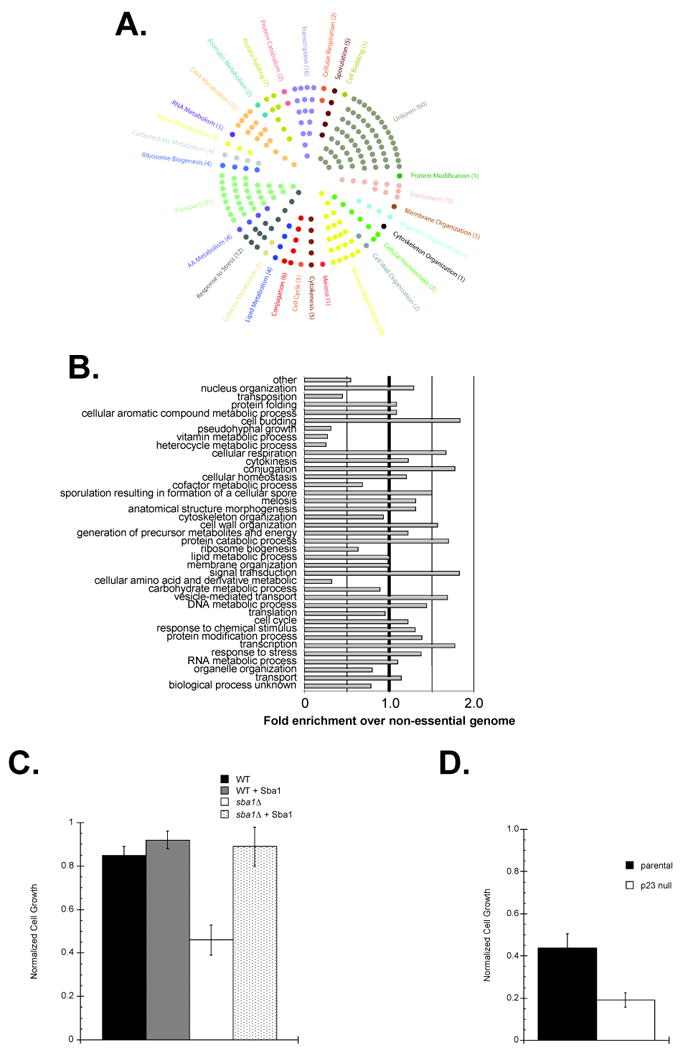
SGA analysis revealed a broad genetic interaction network for Sba1 that included factors involved in vesicle-mediated protein transport. The genes that produced an SSL phenotype with sba1Δ were categorized by a GO Slim analysis. (A) Each hit was assigned to an initial cellular process and displayed or (B) all potential processes were considered for each gene and the enrichments in each category were determined relative to the distribution of all non-essential yeast ORFs. (C) To test if Golgi function was Sba1-dependent parental (WT) and sba1Δ transformants carrying either an empty or an Sba1-expression vector (+ Sba1) were treated with the Golgi transport inhibitor Brefeldin A (BFA) (100 μg mL-1). (D) To check if mammalian Golgi function is p23-dependent, exponentially growing parental or p23 null MEFs were cultured in unsupplemented or BFA-supplemented (50 μg mL-1) media. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.
