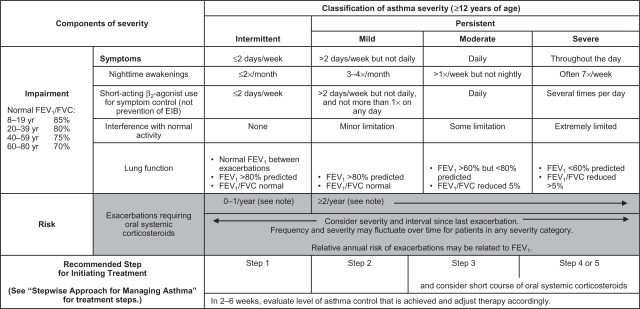
Figure 1.
Methods of classifying asthma severity and initiating treatment in patients 12 years of age and older.
Notes: Level of severity is determined by assessment of both impairment and risk. Assess impairment domain by patient’s/caregiver’s recall of previous 2–4 weeks and spirometry. Assign severity to the most severe category in which any feature occurs. At present, there are inadequate data to correspond frequencies of exacerbations with different levels of asthma severity. In general, more frequent and intense exacerbations (eg, requiring urgent, unscheduled care, hospitalization, or ICU admission) indicate greater underlying disease severity. For treatment purposes, patients who had ≥2 exacerbations requiring oral systemic corticosteroids in the past year may be considered the same as patients who have persistent asthma, even in the absence of impairment levels consistent with persistent asthma. Reproduced from the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute.7
Abbreviations: EIB, exercise-induced bronchospasm; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC, forced vital capacity; ICU, intensive care unit.