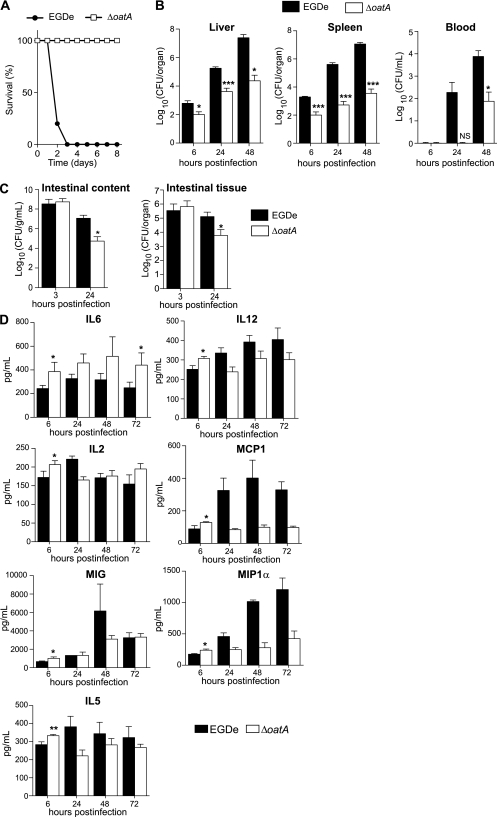
Figure 3.
The ΔoatA mutant has a strongly attenuated virulence in mice and triggers an increased cytokine response early after infection. A, BALB/c mice were challenged by intravenous injection of 106 EGDe (black circles) or ΔoatA (white squares). Survival of infected mice was determined over time (n = 5). B, BALB/c mice were challenged by intravenous injection of a sublethal dose (104 bacteria per mouse) of EGDe (black bars) or ΔoatA (white bars). Colonization of liver, spleen, and blood was followed 6, 24, and 48 hours postinfection. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). C, Transgenic human E-cadherin mice were used as a permissive model for the oral route of infection. These mice were infected with 1010 EGDe (black bars) or ΔoatA (white bars). After 3 hours and 24 hours, mice were euthanized and the number of bacteria in the intestinal lumen and intestinal tissue was determined. Data are means ± SD (n = 3–5). D, BALB/c mice were inoculated intravenously with 5 × 103 bacteria. The liver was dissected and homogenized. Homogenates were assayed using a multiplex immunoassay to determine cytokine level in response to infection with EGDe (black bars) or ΔoatA (white bars). Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Student t test was performed to determine statistical significance: *, **, and *** indicate P < .05, P < .01, and P < .001, respectively.