Fig. 5.
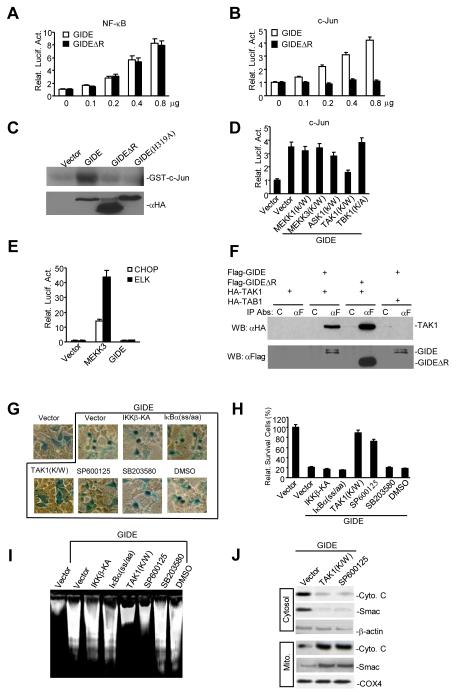
GIDE induces apoptosis through a JNK-dependent pathway. A. Effects of GIDE and GIDEΔR on NF-κB activation. 293 cells (~1×105) were transfected with 0.1 μg of NF-κB-luciferase reporter plasmid and the indicated amounts (in μg) of expression plasmids. Reporter assays were performed sixteen hours after transfection. B&C. Effects of GIDE and its mutants on JNK activation. 293 cells were transfected with GIDE and its mutants as indicated. C-Jun reporter assays (B) or in vitro kinase assays with GST-c-Jun as substrate (C) were performed as described (31). D. GIDE-induced JNK activation is inhibited by TAK1 kinase inactive mutant. 293 cells were transfected with GIDE and the indicated kinase inactive mutants. C-Jun reporter assays were performed as described (47). E. GIDE does not activate CHOP or Elk-1. 293 cells were transfected with GIDE or MEKK3. CHOP and Elk-1 reporter assays were performed as described (31). F. GIDE interacts with TAK1. 293 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG or control mouse IgG. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot with anti-HA (upper panel) and anti-Flag (lower panel) antibodies. G-I. Effects of various mutants or small molecule inhibitors on GIDE-induced apoptosis. 293 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids, treated with SP600125 (20 μM), SB203580 (20 μM) or left untreated as indicated for 16 hours. The cells were stained with X-gal (G), the number of survived blue cells were counted (H), or DNA fragmentation experiments were performed (I). J. JNK is essential for GIDE-induced cytochrome c and Smac release. 293 cells were transfected with GIDE plus control vector or TAK1(K/W), or treated with SP600125 (20 μM) for 16 hours. The cells were fractionated and analyzed by Western blots with the indicated antibodies.