Fig. 3.
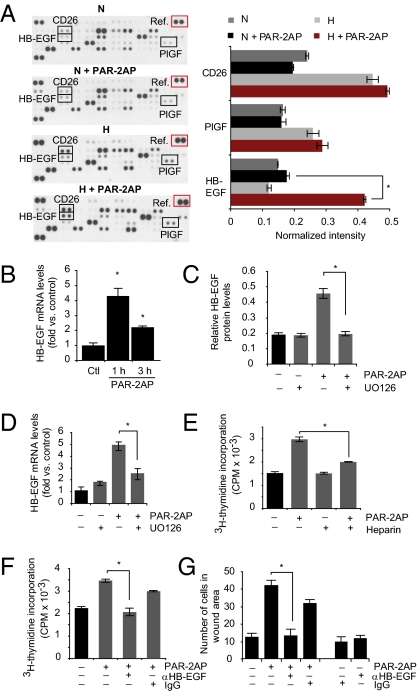
PAR-2–mediated stimulation of hypoxic ECs involves p-ERK1/2–dependent induction of HB-EGF. (A) PAR-2–mediated induction of HB-EGF in hypoxic ECs. Normoxic (N) or hypoxic (H) HUVECs were incubated with or without PAR2-AP (100 μM) for 6 h, and angiogenesis-related proteins were determined by antibody array analysis as described in SI Materials and Methods. Left: Representative immunoblot from three independent experiments. Right: Quantification of placenta growth factor (PIGF), CD26, and HB-EGF levels at the various conditions presented as relative intensities versus array reference (red box). (*P < 0.05.) (B) Hypoxic HUVECs were incubated without (Ctl) or with PAR2-AP (100 μM) for 1 h or 3 h; HB-EGF mRNA expression was determined by qRT-PCR. (*Significant up-regulation vs. control, *P < 0.05.) (C) PAR-2–mediated HB-EGF induction depends on p-ERK1/2. Hypoxic HUVECs were untreated or pretreated with UO126, followed by another incubation period with or without PAR-2AP (100 μM) for 6 h. HB-EGF protein levels were quantified by immunoblotting as in A. (*P < 0.05.) (D) Similar experiment as in C showing HB-EGF mRNA expression as determined by qRT-PCR. (*P < 0.05.) Under the conditions used, UO126 efficiently inhibited PAR-2AP–induced p-ERK1/2 (Fig. S3B). (E–G) Role of HB-EGF in PAR-2–mediated activation of hypoxic ECs. (E) Hypoxic HUVECs were cultured for 24 h, starved for 16 h, and then untreated or treated with PAR-2AP (100 μM) and/or heparin (1 ng/mL) as indicated for another 24 h in the presence of 3 μCi/mL [3H]thymidine. (*P < 0.05.) (F) Similar experiment as in E; hypoxic HUVECs were untreated or treated with PAR-2AP and/or anti–HB-EGF antibody (12.5 μg/mL) as indicated. Nonimmune IgG (12.5 μg/mL) was used as a negative control. (*P < 0.05.) (G) Hypoxic HUVECs were cultured for 24 h and starved for 16 h, and then a scratch wound was formed in confluent monolayers, followed by another 36 h of migration with the treatments indicated. The results are presented as the mean number of cells per wound area ± SD. (*P < 0.05.)