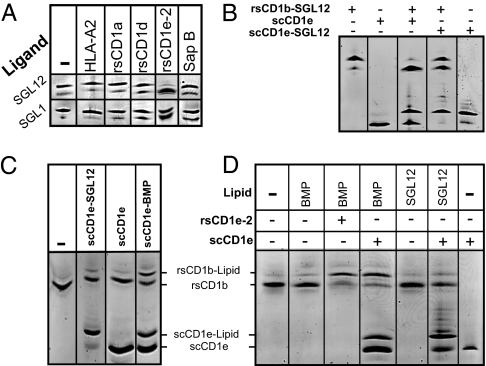
Fig. 3.
CD1e mediates the exchange of lipids with CD1b. (A) rsCD1e-2 induces the dissociation of ligands from CD1b. Purified rsCD1b-SGL12 or rsCD1b-SGL1 was incubated for 30 min at room temperature in the presence or absence of a 3-fold molar excess of HLA-A2, human rsCD1a, or rsCD1d; a 1.5-fold excess of rsCD1e-2; or a 10-fold excess of saposin B, before IEF separation. The incubation mixtures included 0.5× lipid vesicles (Fig. 2). (B) Single-chain CD1e efficiently unloads CD1b-bound lipids. Purified rsCD1b-SGL12 (8 μM) was incubated for 30 min with or without an equimolar amount of scCD1e or scCD1e-SGL12 in the presence of 0.5× lipid vesicles, before IEF separation. (C) Direct transfer of scCD1e-bound lipids to CD1b. Mixtures containing rsCD1b and the indicated scCD1e–lipid complex or unloaded scCD1e were incubated for 10 min at pH 5.0 and 37 °C, before analysis by IEF. (D) CD1e transfers lipids from vesicles to CD1b. BMP or SGL12 vesicles were incubated for 30 min at pH 5.0 with rsCD1b in the presence or absence of rsCD1e-2 or scCD1e, before analysis by IEF. To achieve higher magnification, bands from sCD1e-2 observed at lower pI values (Fig. S6E) are not presented here. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.