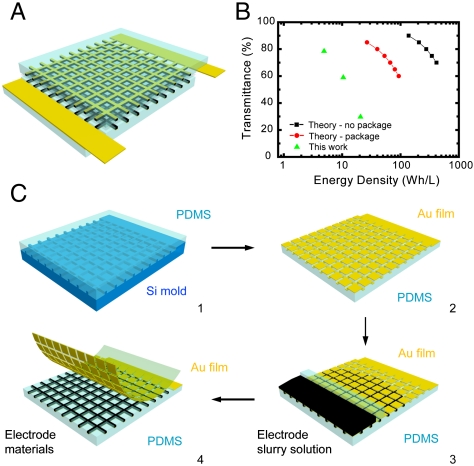
Fig. 1.
(A) The schematic of a transparent battery with grid-like patterned electrodes. In contrast to using thin film electrodes, this concept allows scalable energy storage while maintaining high transparency. The different colors indicate the PDMS substrate (light blue), electrode materials (black), and metal current collector (yellow). (B) The transparency versus volumetric energy density. The black line is only active materials and the red line considers the volume of other components, such as separators, current collectors, and packaging. (C) The process flow of fabricating a transparent battery: (1) Transfer grid patterns from silicon mold to PDMS, (2) evaporate gold current collector onto the PDMS substrate, (3) fill in battery electrode materials by a microfluidics-assisted method, and (4) peel off gold film on top of the PDMS substrate.