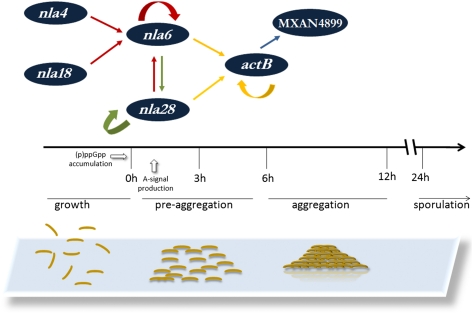
Fig. P1.
An EBP transcriptional cascade controls multicellular development in M. xanthus. Starvation and accumulation of (p)ppGpp trigger the transition from growth to development. The hallmark of the preaggregation stage of development is the accumulation of the quorum signal known as A-signal. Once (p)ppGpp and A-signal reach sufficient levels, cells aggregate and then sporulate. Black lines show the extent of the preaggregation and aggregation stages of development (1–5 h and 6–12 h, respectively). Colored straight arrows represent direct transcriptional regulation, and colored curved arrows represent autoregulation. Note that pairs of EBPs that function at one stage of development directly regulate transcription of an EBP gene important for the next developmental stage. Red arrows indicate EBPs that regulate nla6, green arrows indicate EBPs that regulate nla28, yellow arrows indicate EBPs that regulate actB, and the blue arrow indicates the EBP that regulates MXAN4899.