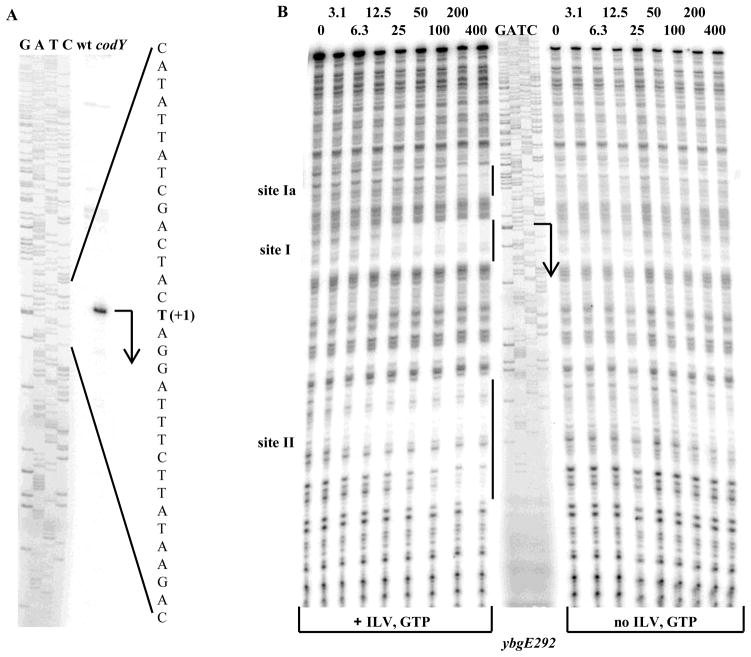
Fig. 2. Determination of the ybgE transcription start point and CodY-binding regions.
A. Primer extension analysis of the ybgE mRNA. Primer oBB102 annealing to the lacZ gene of the ybgE292-lacZ fusion containing the entire ybgE regulatory region was extended with reverse transcriptase using as the template total RNA from fusion-containing strains BB2770 (wt) and BB2771 (codY) grown in the 16 amino acid-containing medium. The sequence of the template strand of the ybgE fragment from pBB1506 determined from reactions primed with oBB102 is shown to the left. The apparent transcription start site of the ybgE gene is in bold and marked by the +1 notation. A bent arrow indicates the direction of transcription.
Additional faint bands observed in the primer extension lanes reflect unspecific binding of oBB102 to DNA and were present even when total RNA used for reverse transcription was isolated from a strain that did not contain the ybgE-lacZ fusion (data not shown).
B. DNase I footprinting analysis of CodY binding to the ybgE regulatory region. The ybgE292p+ DNA fragment labelled on the template strand was incubated with increasing amounts of purified CodY in the presence of 10 mM ILV and 2 mM GTP or in their absence and then with DNase I. The sequence of the ybgE region was determined by using pBB1506 as the template and oBB102 as the primer and is shown in the middle. The apparent transcription start site and direction of ybgE transcription are shown by the bent arrow. The protected areas are indicated by the vertical lines. CodY concentrations used (nM of monomer) are indicated above each lane.